Fig. 5.
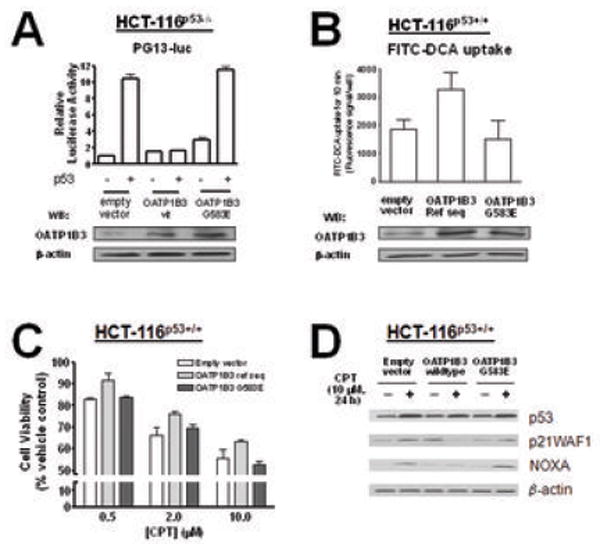
The OATP1B3 variant (G583E) lacking the transport activity confers neither an inhibitory effect on p53 transcriptional activity nor a survival advantage following CPT treatment. A: The results from the p53-responsive PG13-luc reporter assays in HCT-116p53-/- cells demonstrate that the OATP1B3 G583E variant does not affect the transcriptional activity of p53 in contrast to OATP1B3 (wildtype). B: The results from a cellular uptake assay using a fluorescently labeled deoxycholic acid (FITC-DCA, 10 μM) indicate that HCT-116p53+/+ cells stably overexpressing OATP1B3 (wildtype) show an increased cellular uptake of FITC-DCA compared to the cells stably overexpressing the OATP1B3 G583E variant or empty vector controls. C: Overexpression of the OATP1B3 G583E variant does not confer a cell survival advantage following camptothecin (CPT) treatment to HCT-116p53+/+ cells, in contrast to OATP1B3 (wildtype). D: The levels of the p53 downstream targets, P21WAF1 and NOXA are increased following CPT treatment in HCT-116p53+/+ cells stably overexpressing OATP1B3 (wildtype) or empty vector, but not in those stably overexpressing the OATP1B3 G583E variant.
