Figure 7. Schematic representation of torsinA degradation pathways.
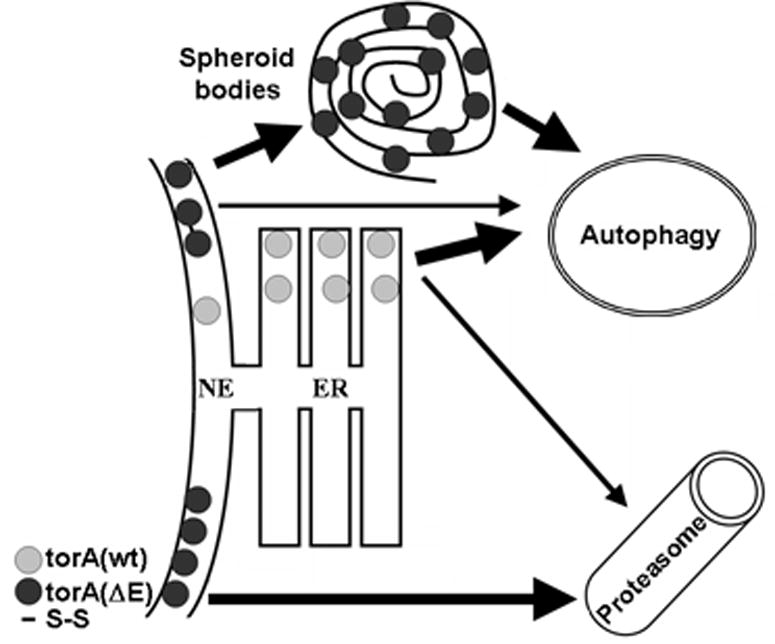
The turnover of torsinA(wt), preferentially located within the ER, is mostly dependent on the actions of autophagy. On the other hand, the NE localization of torsinA(ΔE) targets it for proteasomal degradation when existing as monomers. However, the presence of intermolecular disulfide links in torsinA(ΔE) oligomers would interfere with the retrotranslocation step, requiring autophagy for their clearance. Similarly, torsinA(ΔE) accumulated in spheroid bodies would be degraded through autophagy.
