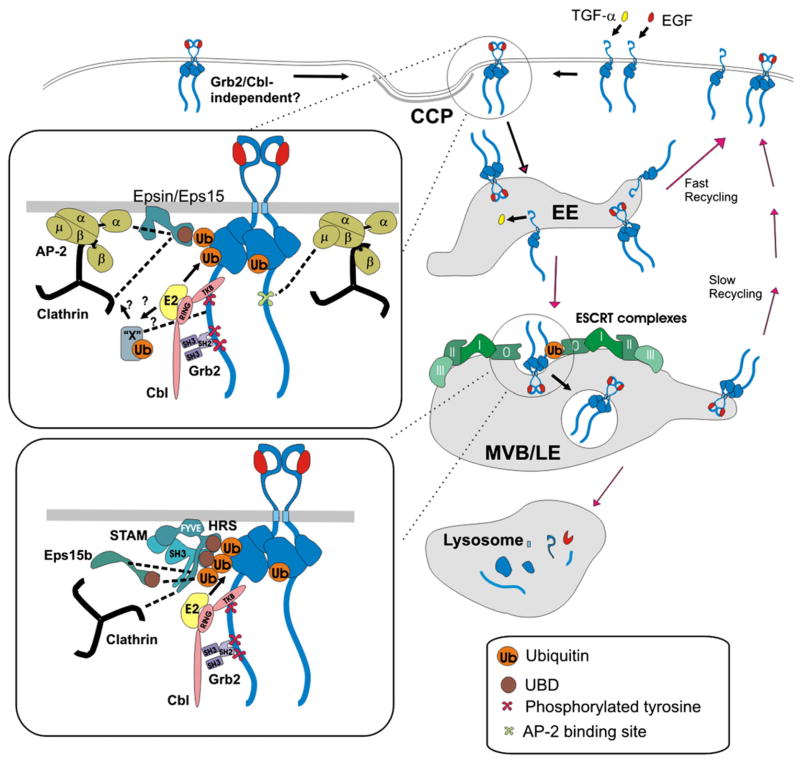
Fig. 2.
A hypothetic model of EGFR endocytosis and intracellular sorting (in the presence of low concentrations of EGF or TGFα). EGF binding to EGFR leads to receptor dimerization and phosphorylation. Grb2–Cbl complex is recruited to C-terminal phosphotyrosine-containing motifs. E2 enzymes (UbcH4/5) are recruited to the RING domain to promote receptor ubiquitination. Ubiquitinated EGFR can be recognized by UBDs of epsin, Eps15 and Eps15R in the plasma membrane and clathrin-coated pits (CCP). These proteins are associated with AP-2 and clathrin heavy chain, a main component of the clathrin triskelion (clathrin). Alternatively, Cbl can mediate ubiquitination of an unknown adaptor protein (“X”) that mediates internalization of EGFR through coated pits by interacting with EGFR and/or clathrin or clathrin-associated proteins. EGFR can directly interact with AP-2 via YRAL and possibly LL motifs. There might be also a Grb2-independent pathway of internalization through coated pits. After internalization EGF-receptor complexes can be rapidly recycled from early endosomes (EE) or remain in these endosomes during their maturation into MVB and late endosomes (LE). In contrast, TGF-α dissociates from EGFR in endosomes, which results in the recycling of the monomeric, inactive receptor. In MVB, ubiquitinated EGFR is engaged into multi-valent interactions with UBDs of the ESCRT-0 complex (HRS and STAM) and associated Eps15b, and then incorporated into internal vesicles of MVB. The concentric ring model of the inward invagination of MVB membrane is depicted. Receptors that are not ubiquitinated can be recycled back to the plasma membrane through the tubular extensions of the limiting membrane of MVB at a slower rate. Recycling of occupied and unoccupied receptors may also involve a late recycling compartment (not shown). MVB fuses with primary lysosomes, which subsequently results in degradation of EGF and EGFR.