Abstract
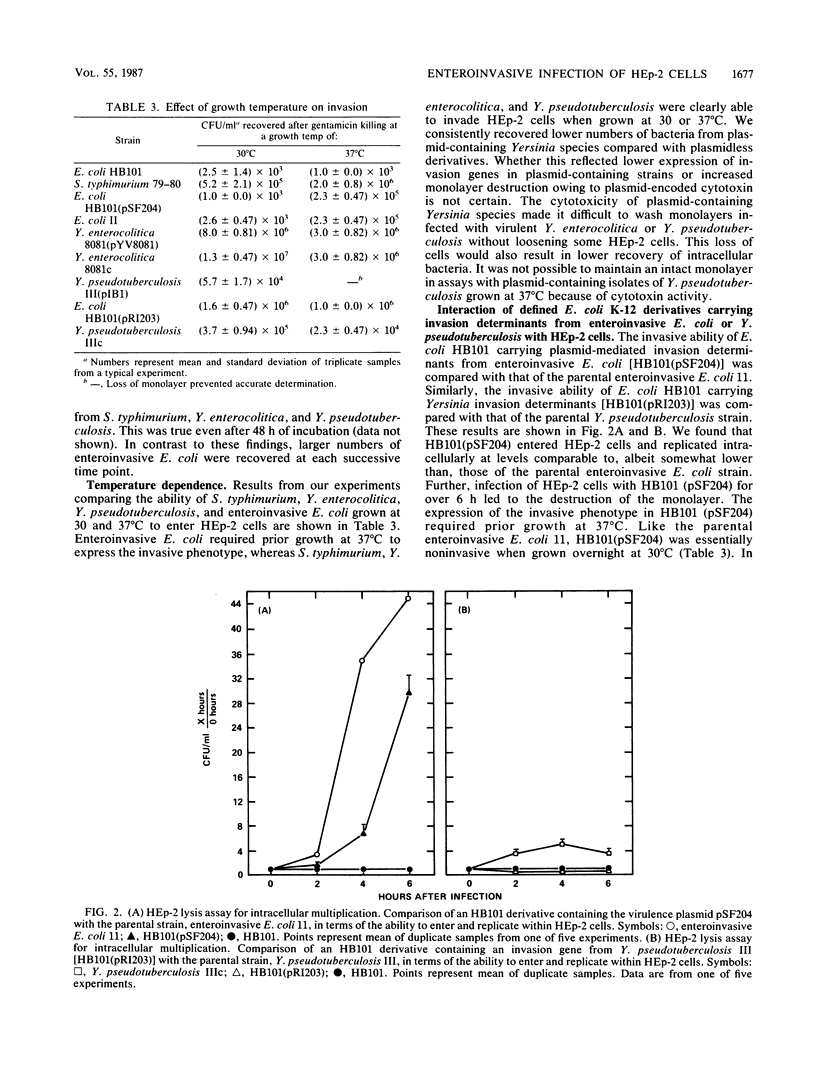
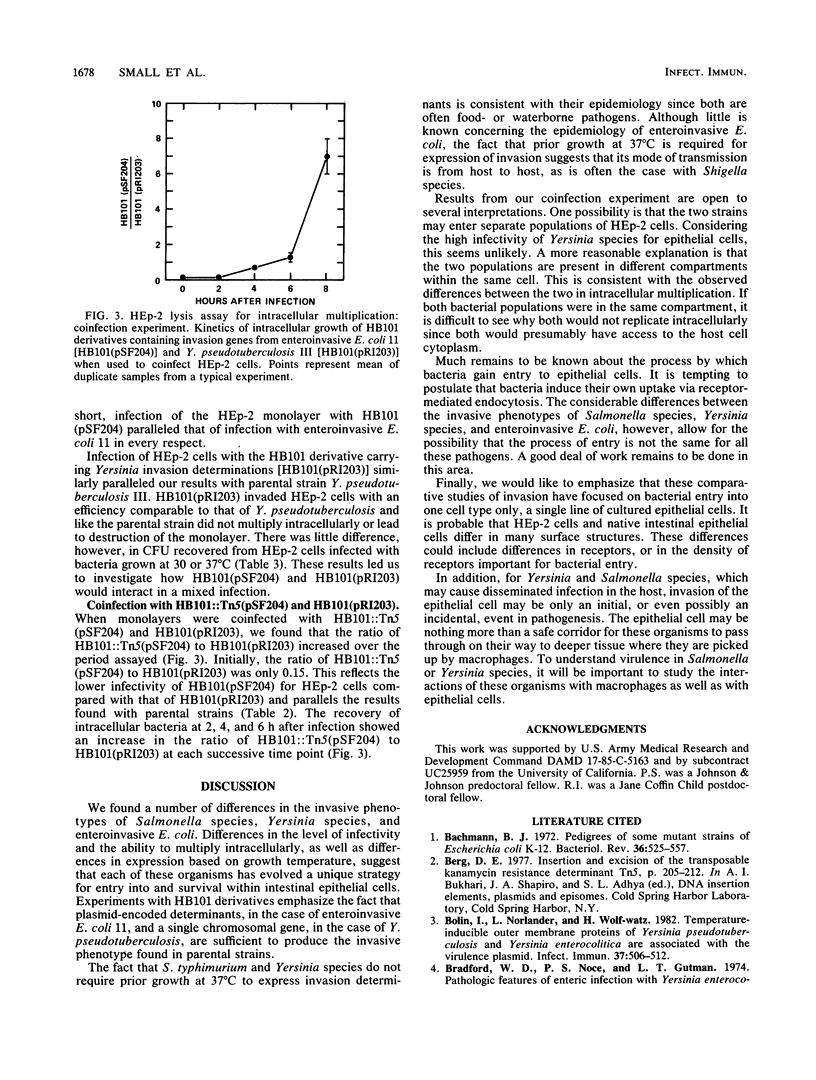
Salmonella typhimurium, enteroinvasive Escherichia coli, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, and Yersinia enterocolitica possess the ability to enter intestinal epithelial cells. We used a quantitative tissue culture model employing HEp-2 cells to compare the abilities of these bacteria to enter epithelial cells. S. typhimurium and Yersinia species were highly infective for HEp-2 cells but were unable to replicate extensively intracellularly. Enteroinvasive E. coli exhibited low infectivity but replicated extensively intracellularly. The growth of enteroinvasive E. coli led to destruction of the HEp-2 monolayer, whereas Yersinia spp. and S. typhimurium were maintained intracellularly for prolonged periods without damage to the monolayer. The ability of enteroinvasive E. coli to enter HEp-2 cells required prior growth at 37 degrees C; neither S. typhimurium nor Yersinia spp. exhibited this temperature dependence for cell entry. An E. coli K-12 derivative containing a 230-kilobase plasmid from enteroinvasive E. coli was constructed. This derivative shared all the invasive characteristics of the parental enteroinvasive strain, suggesting that determinants required for cell entry and intracellular multiplication were at least partially plasmid encoded. An HB101 derivative containing a cloned invasion determinant from Y. pseudotuberculosis was constructed in our laboratory. HEp-2 monolayers were coinfected with these two K-12 derivatives to compare invasion determinants from enteroinvasive E. coli with those of Y. pseudotuberculosis in a common genetic background. Results from these experiments suggest that these organisms reside within separate intracellular compartments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford W. D., Noce P. S., Gutman L. T. Pathologic features of enteric infection with Yersinia enterocolitica. Arch Pathol. 1974 Jul;98(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J. A., Schiemann D. A. HeLa cell infection by Yersinia enterocolitica: evidence for lack of intracellular multiplication and development of a new procedure for quantitative expression of infectivity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.48-55.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., KENT T. H., FALKOW S. ABORTIVE INTESTINAL INFECTION WITH AN ESCHERICHIA COLI-SHIGELLA FLEXNERI HYBRID STRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1374-1382.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Walker W. S., Hatch T. P., Yother J. Plasmid-determined cytotoxicity in Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):788–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.788-794.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Algermissen B., Laufs R. Genetically manipulated virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.105-110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacewicz M., Keusch G. T. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. VIII. Evidence for a translocation step in the cytotoxic action of Shiga toxin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Nov;148(5):844–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.5.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rabert D. K., Svinarich D. M., Whitfield H. J. Association of adhesive, invasive, and virulent phenotypes of Salmonella typhimurium with autonomous 60-megadalton plasmids. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):476–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.476-486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Richardson L. A. The attachment to, and invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: the contribution of mannose-sensitive and mannose-resistant haemagglutinating activities. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):361–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Washington O., Formal S. B. Genetic and physical evidence for plasmid control of Shigella sonnei form I cell surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):207–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.207-214.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McGrath P. P., Carter P. H., Eide E. L. The ability of some Yersinia enterocolitica strains to invade HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1714–1722. doi: 10.1139/m77-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.397-401.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in Shigella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.195-201.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Valtonen V. V., Valtonen M. Role of O-antigen (lipopolysaccharide) factors in the virulence of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):81–85. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Winblad S., Bitsch V. Studies on the interaction between different O-serotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica and HeLa cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Apr;87B(2):141–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Blank H. F., Kingsbury D. T., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of essential plasmid determinants of pathogenicity in Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):297–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. K., Bennett P. M., Falkow S., Dodd H. M. Isolation of a temperature-sensitive derivative of RP1. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout W. R., Formal S. B., Dammin G. J., Giannella R. A. Pathophysiology of Salmonella diarrhea in the Rhesus monkey: Intestinal transport, morphological and bacteriological studies. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jul;67(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgeerts P., Geboes K., Ponette E., Coremans G., Vantrappen G. Acute infective colitis caused by endemic pathogens in western Europe: endoscopic features. Endoscopy. 1982 Nov;14(6):212–219. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.75-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Formal S. B., Sprinz H. Exerimental acute colitis in the Rhesus monkey following peroral infection with Shigella flexneri. An electron microscope study. Am J Pathol. 1968 Mar;52(3):503–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vantrappen G., Geboes K., Ponette E. Yersinia enteritis. Med Clin North Am. 1982 May;66(3):639–653. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P., Waldvogel F. A. Gentamicin antibacterial activity in the presence of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):743–749. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Bromirska J., Mäki M. Enhancement of invasiveness of Yersinia enterocolitica and Escherichia coli in HEp-2 cells by centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):834–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.834-836.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Timmis K. N. A small plasmid in Shigella dysenteriae 1 specifies one or more functions essential for O antigen production and bacterial virulence. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):391–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.391-396.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


