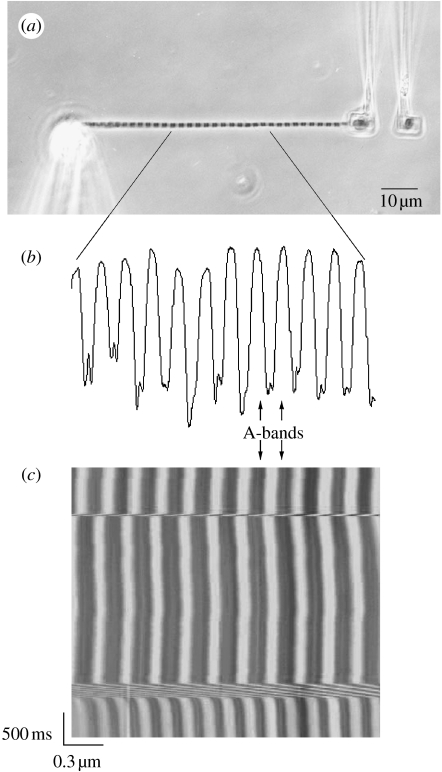
Figure 1.
(a) A myofibril suspended between a glass needle and a pair of microfabricated cantilevers. Note that the sarcomere striation is visible showing the contrast between A- and I-bands. (b) The striation pattern creates a light intensity peak diagram corresponding to the sarcomere bands. Sarcomere length (SL) was measured with an algorithm that calculates the distance between the centroids of the A-bands, representing the SL. In some myofibrils, it was possible to manually track the Z-lines, and the results were used to confirm the SL measurements made with the A-bands. (c) When consecutive peaks (x-axis) are scanned over successive scans (y-axis), a SL–time myogram can be created, during which the behaviour of individual sarcomeres can be tracked during activation, shortening and stretch.