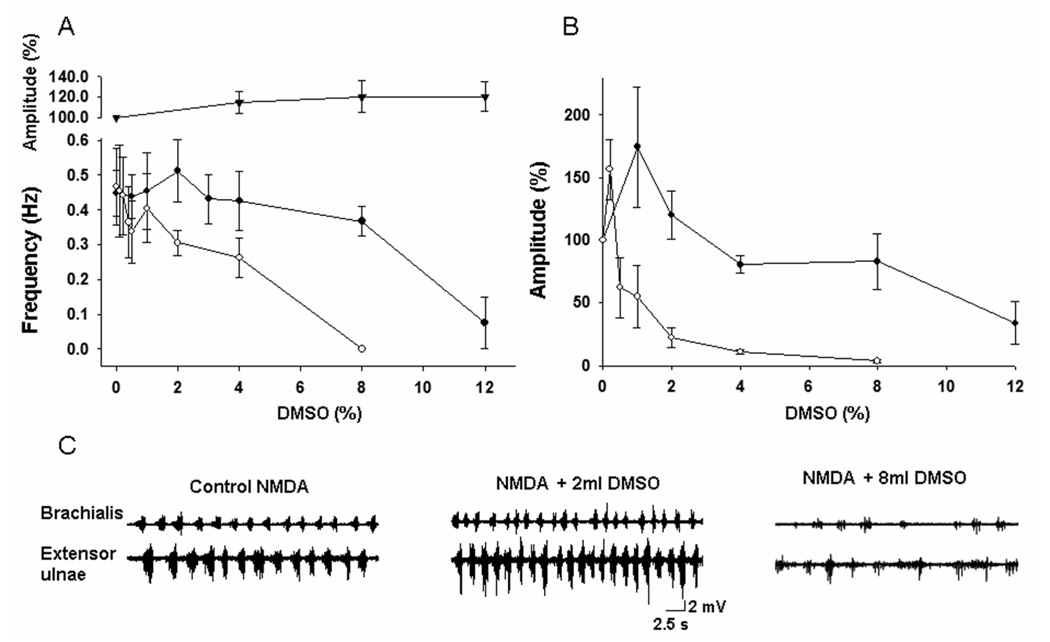
Figure 4. Effects of DMSO on locomotor-like activity.
A: The mean frequency of the walking-like activity was decreased dose-dependently with superfusion of DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=8). The activity induced by glutamate (○) was more sensitive to the inhibitory effects of DMSO than that induced by NMDA (●). In contrast, the amplitudes of the dorsal root reflexes were not significantly affected by DMSO (top curve, mean ± SEM, n=8).
B: The mean amplitude of the walking-like active was more profoundly depressed in a dose-dependent manner. Again, the activity induced by glutamate was more sensitive to the inhibition compared to that induced by NMDA (mean ± SEM, n=8).
C: Examples of dose-dependent inhibition of the walking-like activity by DMSO. Note that depression of the amplitude was more profound than the inhibition of the frequency, consistent with the pooled data shown in panels A and B.