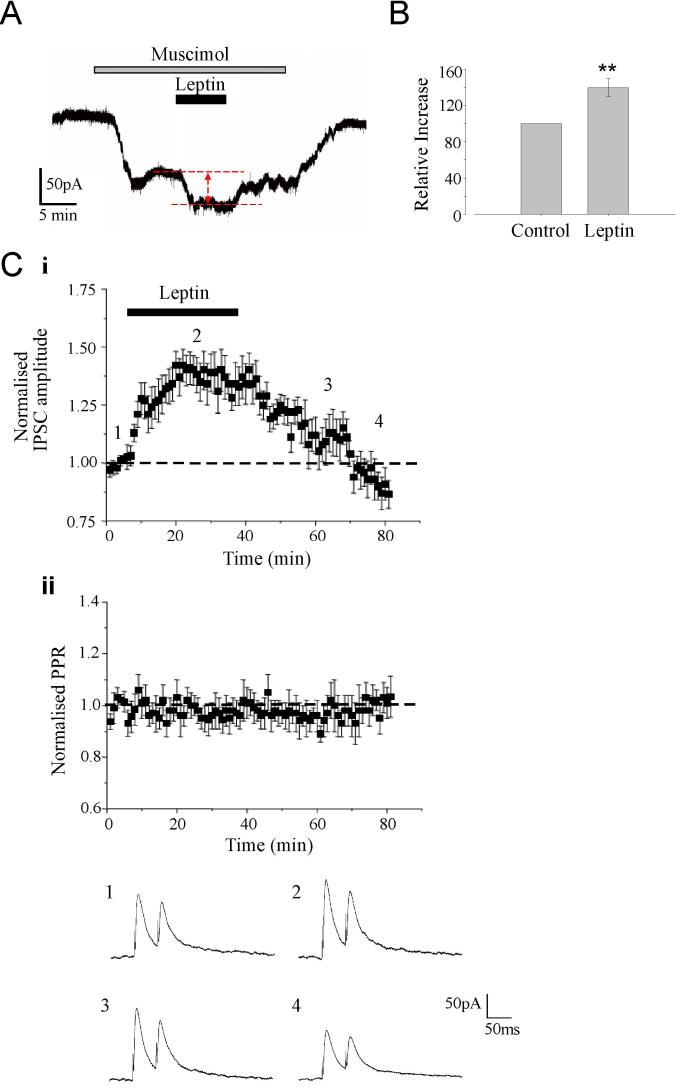
Figure 3. The effects of leptin on eIPSCs involve postsynaptic mechanisms.
A. Representative trace of the inward current evoked by the GABAA receptor agonist, muscimol (1 μM). Application of leptin (50nM) for the time indicated resulted in an increase in the muscimol current that reversed on leptin washout. B. Histogram of pooled data of the mean muscimol current amplitude in control conditions and in presence of leptin. C. The effects of leptin were not accompanied by any marked change in PPR. (i) Plot of the pooled data illustrating the normalized eIPSC amplitude against time. (ii) Plot of the mean PPR against time for the experiments depicted in (i). Below the plots are representative pairs of eIPSCs evoked with a 50 ms inter-stimulus interval obtained at the times indicated in (i).