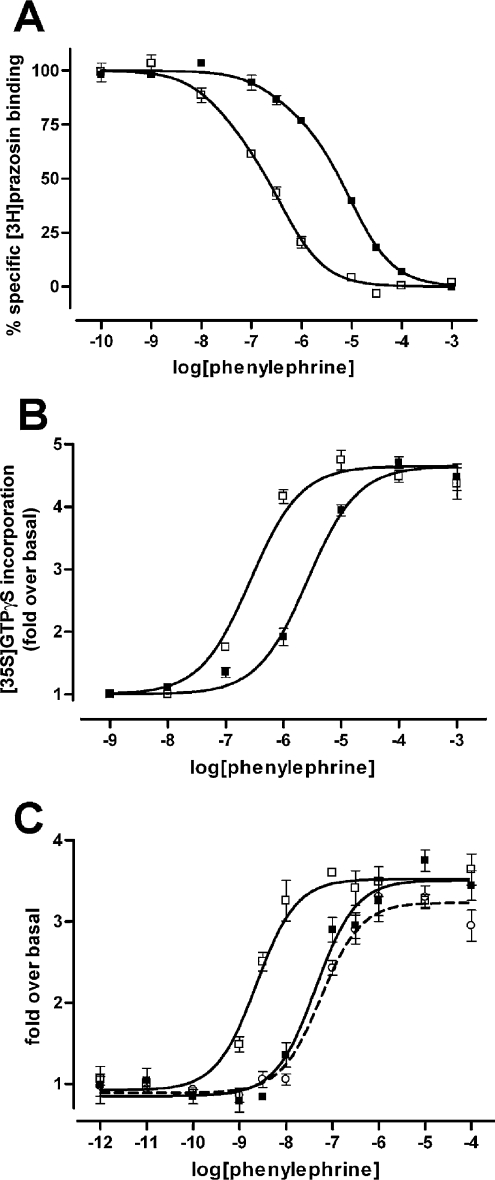
Figure 6. Pharmacological comparisons of FLAG-α1b-adrenoceptor-eYFP and FLAG-α1b-adrenoceptor TMI-TMIV-eYFP.
(A) Ligand-binding characteristics of the wild-type and mutant α1b-adrenoceptor. The capacity of phenylephrine to compete for binding with [3H]prazosin to FLAG-α1b-adrenoceptor-eYFP (■) and FLAG-α1b-adrenoceptor TMI-TMIV-eYFP (□) was assessed. (B) Stimulation of [35S]GTP[S] binding by phenylephrine in Gαq/Gα11 immunoprecipitates from membranes of HEK-293 cells stably expressing FLAG-α1b-adrenoceptor-eYFP (■) and FLAG-α1b-adrenoceptor TMI-TMIV-eYFP (□). (C) Intracellular calcium mobilization induced by phenylephrine in cells stably expressing FLAG-α1b-adrenoceptor-eYFP (■) and FLAG-α1b-adrenoceptor TMI-TMIV-eYFP previously treated with 10−7 M prazosin (□). Complete removal of prazosin after the overnight period was assessed by testing the response of the wild-type receptor after treatment and washout (open circles). All graphs are representative results from at least three independent experiments.