Figure 2.
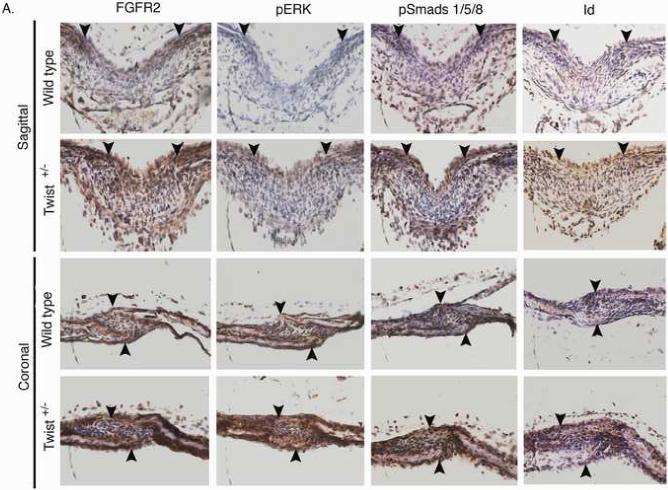
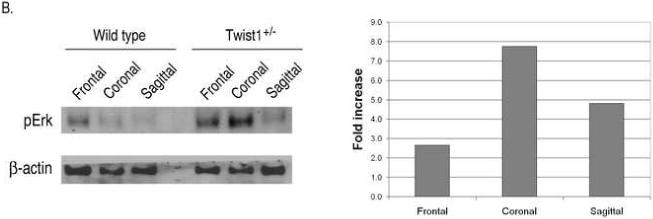
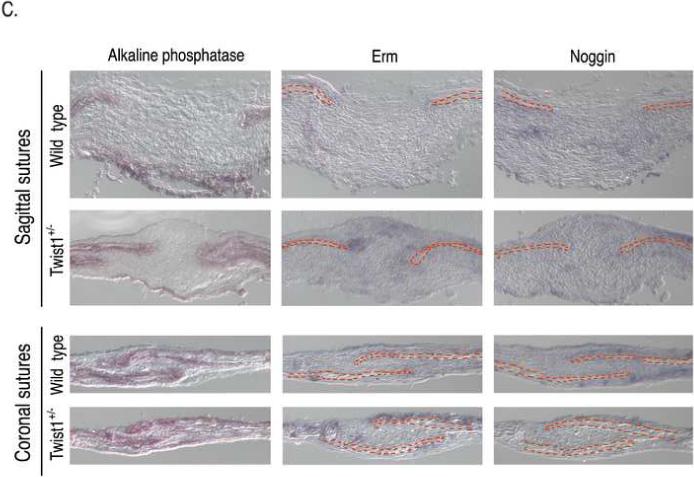
Increased FGF and BMP signaling in the sutures of Twist1+/− mice. (A) Immunohistochemistry for FGFR2, phospho-ERK1/2, phospho-smad1/5/8, and Id1 proteins in the sagittal and coronal sutures of wild type and Twist1+/− P1 mice. Arrow heads indicate the osteogenic fronts. Analysis of at least 3 mice of each genotype was performed, and representative data is shown. Note the extended staining for all of these throughout the sutures of Twist1+/− mice, while they are primarily restricted to the osteogenic fronts in wild type mice. (B) Western blot analysis of phopho-Erk1/2 in wild type and Twist1+/− sutures. Protein extracts from dissected frontal, coronal, and sagittal sutures from two P1 wild type or Twist1+/− mice were pooled and analyzed by western blot analysis for phopho-Erk1/2 and β-actin. The bar graph shows the fold change in phospho-Erk1/2 for each suture between wild type and Twist1+/− mice when corrected for β-actin expression. (C) in situ hybridization analysis of erm and noggin expression in the sagittal and coronal sutures of wild type and Twist1+/− P1 mice. The red dotted lines outline the calvaria bones.
