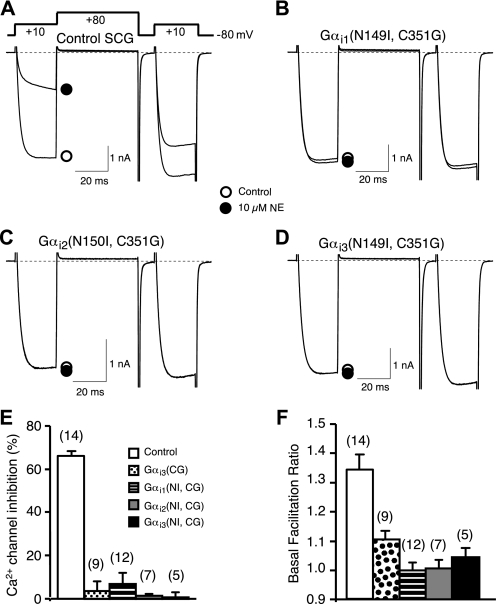
FIGURE 5.
GoLoco-insensitivity mutation does not alter the ability of Gαi to buffer free Gβγ subunits. A-D, superimposed Ca2+ current traces evoked with a double-pulse voltage protocol in the absence (open circle) or presence of 10 μm NE (filled circle) from control (A), Gαi1(N149I, C352G) (B), Gαi2(N150I, C353G) (C), and Gαi3(N149I, C352G) (D) expressing SCG neurons. Currents were evoked every 10 s. The dashed lines indicate the zero current level. E, summary graph of Ca2+ current inhibition by 10 μm NE from control neurons and neurons expressing Gαi1(N149I,C352G), Gαi2(N150I,C353G), or Gαi3 (N149I,C352G). Ca2+ current inhibition was measured 10 ms after initiation of the test pulse (+10 mV) in the absence or presence of 10 μm NE. F, basal facilitation from control neurons or neurons expressing Gαi1(N149I,C352G), Gαi2(N150I,C353G), or Gαi3(N149I,C352G). Basal facilitation was calculated as the ratio of Ca2+ current amplitude determined from the test pulse (+10 mV) occurring after and before the +80 mV conditioning pulse. E and F, bars represent mean±S.E.M. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of neuron tested. The mean for all experimental conditions (colored bars) was different (p < 0.05) from the control condition (open bar) as determined by one-way analysis of variance followed by Neuman-Keuls multiple comparison test. Means among experimental groups were not different.