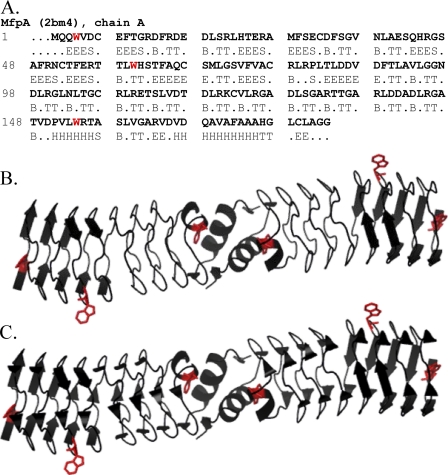
FIGURE 1.
A, the amino acid sequence of the MfpA chain A with DSSP (11) assigned secondary structure (H, α-helix; B, isolated β-bridge; E, extended strand participating in β-ladder; T, hydrogen bonded turn; S, bend; R (dots), no assigned structure). B, a ribbon diagram of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis MfpA dimer (2). The two α-helices at the C termini of each monomer are shown. The β-strands are shown as long arrows. The bends, isolated β-bridges, and residues with no assigned structure are depicted as “unordered” according to the secondary structure types calculated from CD spectra. C, the ribbon diagram of MfpA depicting the isolated β-bridges (short arrows) along with other types of the secondary structures shown in B. The tryptophan residues whose fluorescence was monitored are highlighted in red.