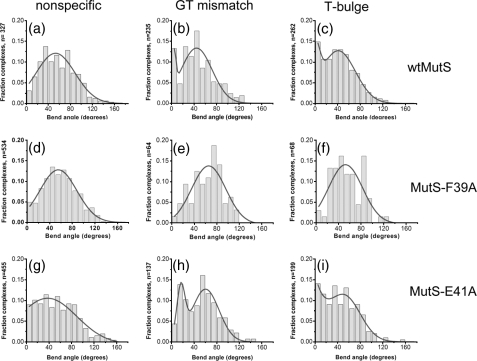
FIGURE 2.
Histograms of DNA bend angles induced by wtMutS (top row), MutS-F39A (middle row), and MutS-E41A (bottom row). Distributions of bend angles are shown for wtMutS bound to homoduplex (nonspecific) DNA (a), a GT mismatch (b), and a T-bulge (c); for MutS-F39A bound to nonspecific DNA (d), a GT mismatch (e), and a T-bulge (f); and for MutS-E41A bound to nonspecific DNA (g), a GT mismatch (h), and a T-bulge (i). The number of complexes (n) analyzed for each distribution is shown on the y axis. The distributions for the nonspecific DNA are determined from MutS proteins bound to homoduplex sites on the 783GT and 783T-bulge DNA fragments. The data for the distribution for wtMutS bound to a T-bulge are taken from reference (9). Complexes in which more than one MutS protein was bound internally to the DNA were not included in these distributions. The curves drawn in a and d--g are single Gaussian fits to the data, and those drawn in b, c, h, and i are double Gaussian fits to the data. For the single Gaussian fits, fitting the bend angle distributions to a sum of two Gaussians does not significantly improve the fits, and a binomial distribution analysis shows no peak at 0° for these data sets (a and d--g). In contrast, a binomial distribution analysis of each of the plots in b, c, and i as well as of the plot in h indicates that the peak at 0° (in b, c, and i) and the peak at 15° (in h) are significant with p = 5 × 10-10, 6 × 10-8, 5 × 10-6, and 7 × 10-12, respectively. In addition, for complexes bound at the specific GT mismatch site, the bend angle shift from 0° for wtMutS to 15° for MutS-E41A is very significant (p = 2 × 10-32, based on normal distribution significance test). For MutS-F39A, a relatively small number of complexes are observed at specific sites (e and f) because of the loss of binding specificity, resulting in greater error in these fits; however, there is clearly no significant population of unbent complexes.