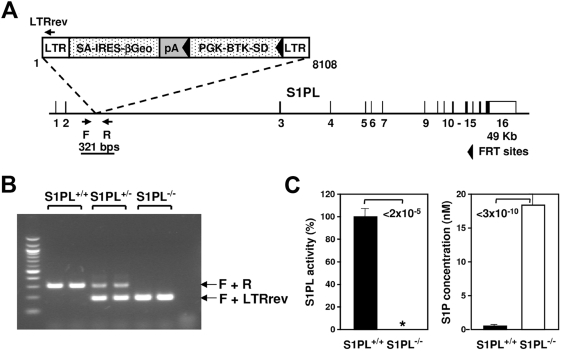
Figure 1. Generation of S1PL mutant mice.
(A) Gene trap mutation of the S1PL gene. The insertion occurred within intron 2 of the S1PL gene (NM_009163). LTR, viral long terminal repeat; SA, splice acceptor sequence; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; βGeo, fusion of beta-galactosidase and neomycin phosphotransferase genes; pA, polyadenylation sequence; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase-1 promoter; BTK-SD, Bruton's tyrosine kinase splice donor sequence. (B) Genotyping strategy. Primers F (5′-TGTAGCAGGCTTTCTTAACTCTGG-3′) and R (5′-TTGGGAAGGTCCTGGTCATTACT-3′) flank the genomic insertion site and amplify a product of 321 nucleotides representing the Wt allele. The LTRrev primer (5′-ATAAACCCTCTTGCAGTTGCATC-3′), complementary to the gene trapping vector, amplifies a 193 nucleotide mutant allele in conjunction with primer F. (C) S1PL activity and S1P concentration were measured in spleen samples of the indicated mice. Enzyme activity was normalized to the mean of the Wt values; 100% corresponds to 172,898±15,344 cpm/mg/hr. Data were pooled from 2 experiments using 4–8 mice of each genotype, and data are presented as mean±SEM. * Activity was below the sensitivity of detection.