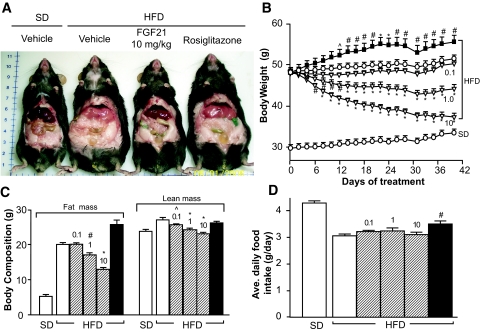
FIG. 1.
Reversal of high-fat diet–induced obesity by recombinant FGF21 in DIO mice. DIO mice were treated with recombinant murine FGF21 intraperitonally at doses of 0 (vehicle), 0.1, 1, or 10 mg · kg−1 · day−1 divided into two daily injections. An additional group of DIO mice was treated with rosiglitazone formulated in the high-fat diet to provide a dose of ∼4 mg · kg−1 · day−1. Mice on standard diet (SD) were included as controls and injected intraperitonally with vehicle. A: Photograph of representative mice either fed standard diet and administered vehicle or fed high-fat diet and administered vehicle, 10 mg · kg−1 · day−1 FGF21, or rosiglitazone for 6 weeks. B: Body weight monitored throughout the treatment. C: Body composition analyzed after 27 days of treatment. D: Average daily food intake during 6 weeks of treatment. Vehicle (open circles or open bars); FGF21 (open triangles or striped bars; 0.1, 1, and 10 denote FGF21 doses in mg · kg−1 · day−1); rosiglitazone (black squares or black bars). All data are means ± SE, n = 10 per group, ∧P < 0.05; #P < 0.01; *P < 0.001 vs. vehicle-treated high-fat diet mice. (Please see http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/db08-0392 for a high-quality digital representation of this figure.)