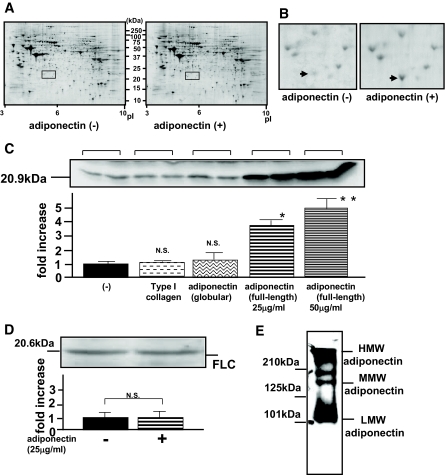
FIG. 1.
Effects of incubation with HMW adiponectin on primary cultured skeletal muscles. Primary cultured murine skeletal muscles were incubated for 12 h in the presence (+) or absence (−) of adiponectin (25 μg/ml). A: Whole images of Coomassie brilliant blue–stained gels for two-dimensional electrophoresis in the absence (left) or presence (right) of adiponectin. B: Magnified images of two-dimensional electrophoresis revealing a spot apparently altered by adiponectin treatment (arrows). Three two-dimensional electrophoresis sets yielded similar results. C–E: After incubation with the indicated ligands, primary cultured skeletal muscle cells were lysed in ice-cold lysis buffer and centrifuged at 14,000g for 10 min at 4°C. Supernatants including tissue protein extracts were resolved on 10% SDS-PAGE, followed by electrophoretic transfer to a nitrocellulose membrane. Membranes were incubated for 1 h at room temperature with antibody against mouse FHC (C) or FLC (D). E: The recombinant full-length human adiponectin, which was expressed in a mouse myeloma cell line NS0, was resolved on 7.5% SDS-PAGE under nonreducing conditions and investigated by immunoblotting with anti-adiponectin antibody. After blotting with the indicated secondary antibody, detection was performed using an electrochemiluminescence chemiluminescent kit according to the manufacturer's instructions. Representative data from four independent experiments are presented. *Significant difference (P < 0.05) relative to FHC expression in control cells. **Significant difference (P < 0.05) relative to FHC expression with 25 μg/ml of adiponectin. N.S., not significant relative to control cells in the absence of adiponectin.