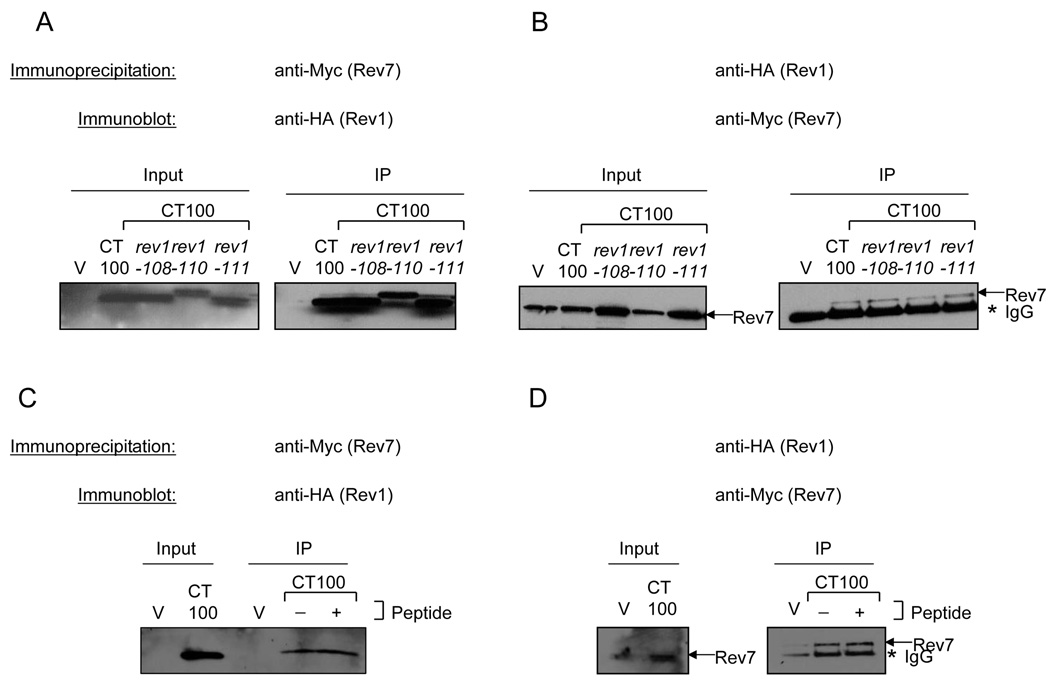
Fig. 10.
Effect of mutations in conserved C-terminal motifs on the Rev1-Rev7 interaction. (A) Lysates from the Rev7-13Myc strain transformed with the empty vector (V) or expressing WT and the indicated mutant derivatives of CT100 were immunoprecipitated using an anti-Myc antibody to pull down Rev7 and immunoblotted with an anti-HA antibody to detect Rev1. A portion of the lysate was run as the input. (B) Lysates from the Rev7-13Myc strain transformed with the empty vector (V) or expressing WT and the indicated mutant derivatives of CT100 were immunoprecipitated using an anti-HA antibody to pull down the Rev1 C-terminal fragments and immunoblotted with an anti-Myc antibody to detect Rev7. A portion of the lysate was run as the input. (C) Immunoprecipitations performed as above with an anti-Myc antibody (C) or an anti-HA antibody (D) were carried out in the presence or absence of the Rev1 peptide described in the materials and methods. Immunoprecipitated proteins were immunoblotted using an anti-HA antibody (C) or an anti-Myc antibody (D).