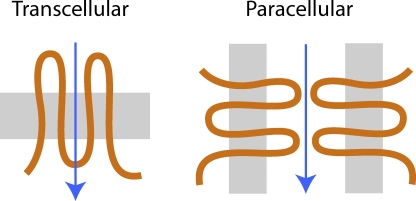
Figure 1.
Comparison of the different transepithelial transport routes. Transcellular/transmembrane channels (left) mediate ion transport (arrow) perpendicular to the plane of the lipid bilayer (gray), with the pore wall formed predominantly by intramembrane domains of the channel polypeptide (orange). Paracellular pores such as claudins (right) mediate transport parallel to and extracellular to the lipid bilayer, with the pore walls presumably constituted by the extracellular domains of claudin polypeptides.