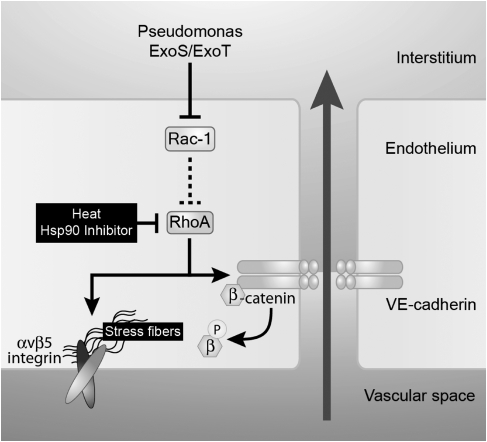
Figure 9.
Schematics of the effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the lung endothelial barrier. Our model diagrams the P. aeruginosa–induced signaling pathway that leads to an increase in lung endothelial permeability. ExoS and ExoT, two cytotoxins from the type III secretion system of P. aeruginosa, increase lung endothelial permeability via the inhibition of Rac1 and the activation of the RhoA/αvβ5 signaling.