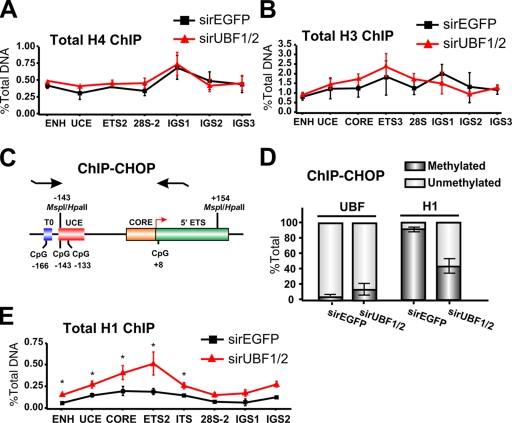
Figure 6.
Loss of UBF1/2 leads to an increase in total levels of histone H1 associated with rRNA genes. (A and B) Depletion of UBF does not alter the total levels of core histones associated with rDNA. qChIP analysis of the rRNA genes in siRNA-EGFP– or -UBF1/2–transfected NIH3T3 cells using antibodies against total histone H4 (A) or total histone H3 (B). Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR as described in Fig. 1 D (n = 3). (C) Schematic of the ChIP-CHOP assay representing the murine rDNA promoter and the 5′ ETS region as in Fig. 4 A with the position of restriction enzyme sites and primers used for qRT-PCR indicated. (D) ChIP-CHOP assay of UBF or histone H1 ChIPs from siRNA-EGFP– or -UBF1/2–transfected NIH3T3 cells. Samples were either mock digested or digested with HpaII. The relative level of HpaII-resistant methylated rDNA was determined by qRT-PCR using the core primers, and the difference was designated as unmethylated rDNA (n = 4). (E) qChIP analysis of the rRNA genes in siRNA-EGFP– or -UBF1/2–transfected NIH3T3 cells using antibodies to total histone H1. Chromatin samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR as described in Fig. 1 D (n = 3; *, P < 0.05). Mean ± SEM (error bars).