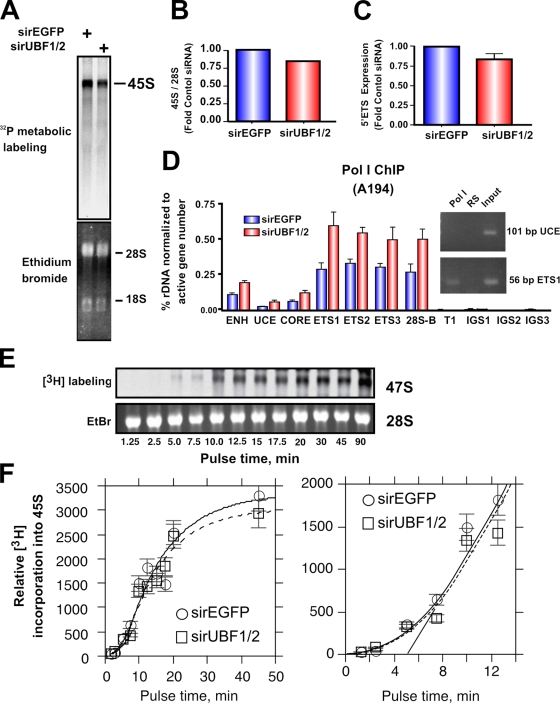
Figure 8.
UBF1/2 depletion causes a modest decrease in net rDNA transcription. (A) NIH3T3 cells transfected with siRNA-EGFP or -UBF1/2 and incubated in phosphate-free DME for 2 h and in phosphate-free DME/FBS containing 0.125 mCi/ml [32P]orthophosphate for 30 min. 32P-labeled cellular RNAs were resolved on 1.2% MOPS-formaldehyde gels and exposed on a PhosphoImaging screen. Total levels of 28S and 18S rRNAs were detected by ethidium bromide staining. (B) 45S rRNA levels in A were quantitated and normalized to corresponding total 28S levels. (C) Total RNA was extracted from siRNA-EGFP– or -UBF1/2–transfected NIH3T3 cells and normalized to an equal number of cells for each sample, and 45S rRNA precursor levels were determined by reverse transcription qRT-PCR using primers to the 5′ ETS (n = 3). (D) qChIP analysis of Pol I (A194 subunit) binding to the rDNA. Pol I enrichment was calculated as described in Fig. 1 D and normalized to the number of active rRNA genes as determined by psoralen cross-linking experiments in Fig. 2 B (n = 3). A representative ethidium bromide gel showing the amount of UCE and ETS1 products amplified after 22 PCR cycles. (E) UBF depletion does not affect Pol I elongation rates in NIH3T3 cells. NIH3T3 cells were transfected with siRNA-EGFP or -UBF1/2 and labeled with 10 μCi [3H]uridine for the indicated times. 3H-labeled cellular RNAs were extracted and resolved on 1% formaldehyde gels, transferred to membrane, and exposed to x-ray films. Total levels of 28S rRNAs were detected by ethidium bromide (EtBr) staining. (F) Duplicate analyses of 3H-labeled 45S rRNA in E were quantitated and normalized to corresponding total 28S levels (EtBr). The curves fitted to the data were calculated as previously shown (Stefanovsky et al., 2006a). The mean per gene elongation time was estimated to be 5 min by extrapolation of the linear phase of incorporation onto the time axis. ENH, enhancer; ITS, internal transcribed spacer; T, terminator region. Mean ± SEM (error bars).