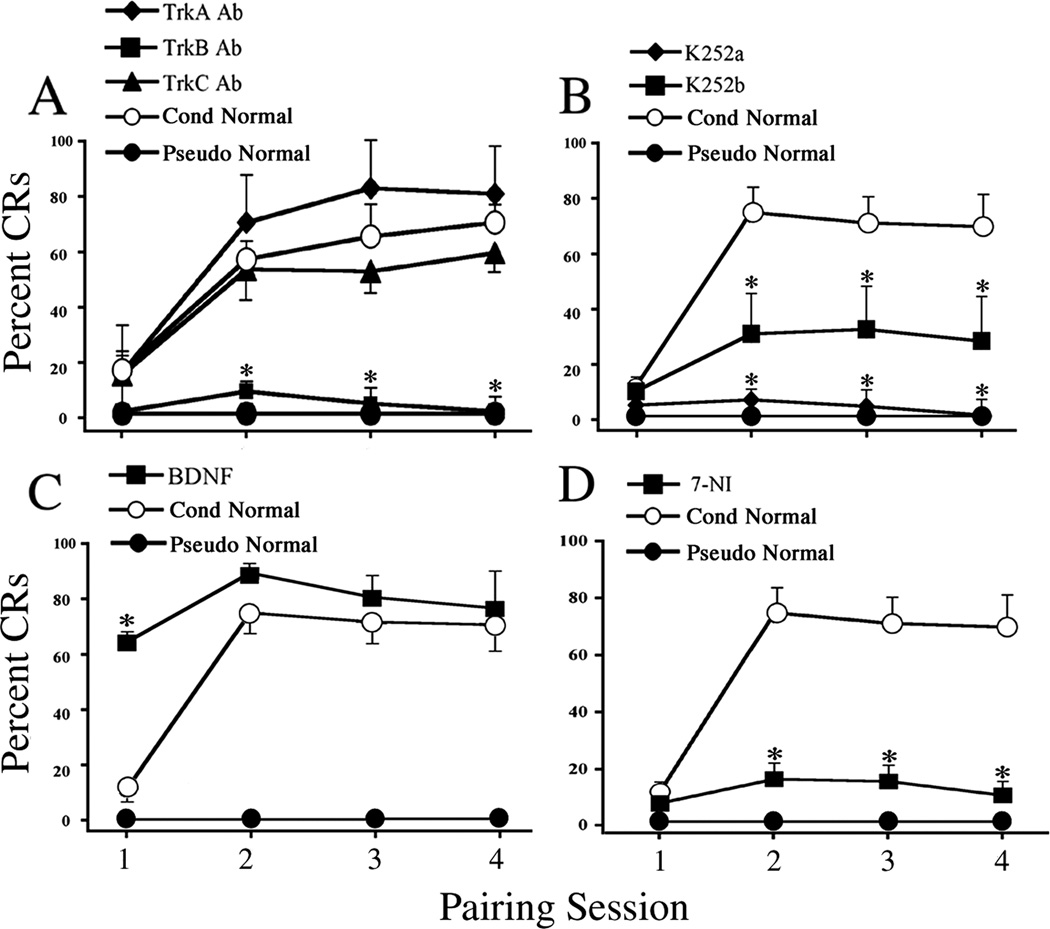
Fig. 3. BDNF-TrkB and nitric oxide are required for acquisition of in vitro conditioning.
(A) Preparations treated with TrkA or TrkC Ab (5 µg/ml) overnight were able to undergo conditioning and express CRs similar to conditioned preparations, while conditioning was not established in preparations treated with TrkB Ab (5 µg/ml) and was comparable to the pseudoconditioned group. (B) CRs were abolished by K252a treatment (200 nM), and were also significantly attenuated by K252b (200 nM) compared to conditioning. (C) BDNF treatment (100 ng/ml) prior to training significantly facilitated the acquisition of CRs in the first pairing session compared to conditioning in normal saline. (D) Application of 7-NI, a selective NOS inhibitor, attenuated the acquisition of conditioning. * indicates significant differences compared with the conditioned group.