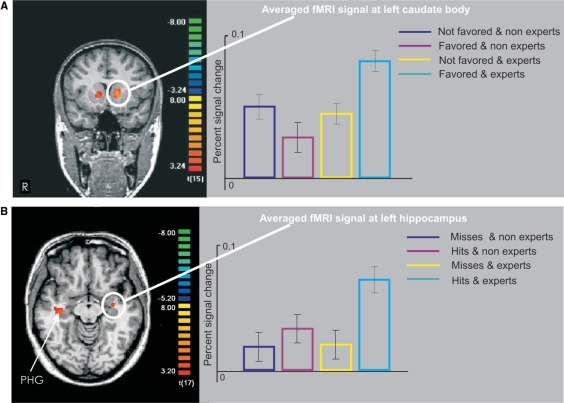
Fig. 3.
Persuasive expertise effects on attitudes and memory (A) The interaction of perceived celebrity expertise with SAE. The left panel depicts the interaction in the caudate nucleus. The right panel depicts the averaged fMRI signal for the left caudate nucleus cluster. The averaged fMRI signals for not favoured objects (with low estimates of purchase incidence) that followed non-experts (dark blue), favoured objects (with high estimates of purchase incidence) that followed non-experts (pink), not favoured objects that followed experts (yellow) and favoured objects that followed experts (light blue) are displayed. The averaged fMRI signals were calculated for all significant voxels within the cluster. The error bars depict standard errors of the mean. n = 16. (B) The interaction of perceived celebrity expertise with subsequent recognition memory (SME). The left panel depicts the interaction in the left hippocampus/parahippocampal cortex. The right panel depicts the fMRI signal for the left parahippocampal cluster. The averaged fMRI signals for subsequent misses (objects) that followed non-experts (dark blue), subsequent hits that followed non-experts (pink), subsequent misses that followed experts (yellow) and subsequent hits that followed experts (light blue) are displayed. PHG, parahippocampal cortex. n = 18.