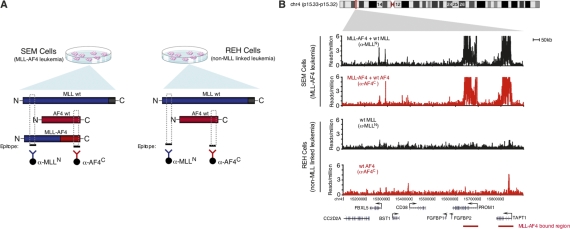
Figure 1.
Mapping MLL-AF4 fusion protein-binding sites in human leukemia cells. (A) Schematic diagram of strategy for mapping MLL-AF4 fusion protein-binding sites. SEM precursor B acute leukemia cells express the MLL-AF4 fusion protein. REH precursor B acute leukemia cells express only endogenous AF4 and MLL1. The N terminus of MLL (blue) is recognized by ChIP antibody anti-MLL-N (blue) and immunoprecipitates both wild-type MLL and MLL-AF4 fusion protein in SEM cells. The C terminus of AF4 (red) is recognized by ChIP antibody anti-AF4-C and immunoprecipitates both wild-type AF4 and MLL-AF4 fusion protein in SEM cells. Wild-type AF4 and MLL-N are immunoprecipitated by anti-AF4-C and anti-MLL-N, respectively. (B) Binding of AF4 (red) and MLL-N (black) in SEM cells (top panels) and REH cells (bottom panels) as determined by ChIP-seq. Binding profiles are shown across an 800-kb portion of the genome surrounding the PROM1 gene (gene models shown in black below graph; a black arrow indicates transcription start sites). MLL-AF4 fusion protein binding is indicated by a red bar.