Table 2.
The structure, cytotoxicity and lipid typology of phosphoramide analogues.
phosphoramide general structure 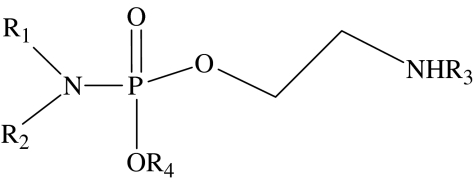
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| compound number | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | EC50/μMa | lipid typologyb |
| 14 | C6H13 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 1000 | undetermined |
| 15 | C12H25 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 230 | type I |
| 16 | C16H33 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 110 | type I |
| 17 | C18H37 | H | CH3 | CH3 | 140 | type I |
| 18 | oleyl | H | CH3 | CH3 | 130 | type I |
| 19 | C18H37 | H | CH3 | C2H5 | 40 | type I |
| 20 | C6H13 | C6H13 | CH3 | CH3 | 140 | undetermined |
| 21 | C3H7 | C15H31 | CH3 | CH3 | 23 | type I |
| 22 | C6H13 | C12H25 | CH3 | CH3 | 77 | undetermined |
| 23 | C12H25 | H | H | CH3 | 250 | type I |
cyclic phosphoramide general structure 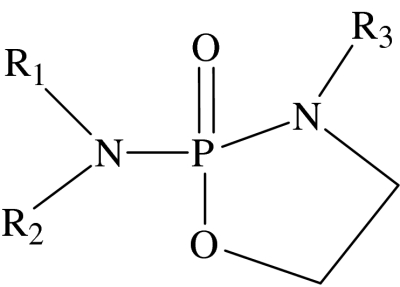
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| compound number | R1 | R2 | R3 | EC50/μMa | lipid typologyb |
| 24 | C16H33 | H | CH3 | 750 | type 0 |
| 25 | C6H13 | H | H | 700 | undetermined |
| 26 | C12H25 | H | H | 20 | type 0 |
| 27 | C16H33 | H | H | 60 | type 0 |
A standard error of ±10% should be applied when interpreting these data.
Lipid typologies were determined by polarizing optical microscopy; those in italics were deduced because the typology of structurally similar compounds is known; some typologies were undetermined because the solubility of the compounds in aqueous solution was too low.
