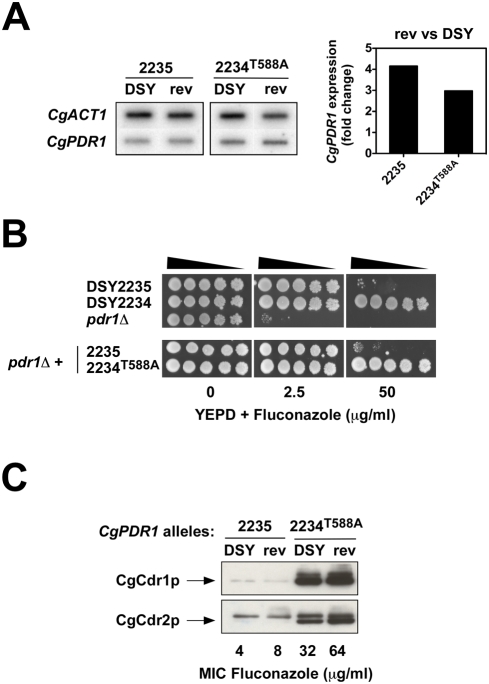
Figure 4. Effect of CgPDR1 expression on azole resistance.
(A) Expression of CgPDR1 in a matched pair of azole-susceptible and azole-resistant isolates (DSY2235 and DSY2234), in revertant strains (“rev”) overexpressing CgPDR1 alleles from an episomal plasmid in a pdr1Δ mutant derived from DSY562 (SFY53). CgPDR1 alleles present in each strain (“DSY” for clinical strains and “rev” for revertant strains) were named according to their strain number origin. RNA was isolated from log phase cultures, slot-blotted to membranes, and hybridized with the indicated gene probes. CgACT1 served as internal control. Signals obtained in blotted membranes were quantified by counting radioactivity by phosphor imaging. Signals obtained for CgPDR1 were normalized with CgACT1 and substracted from background. Expression values represent the increase of CgPDR1 expression in revertant strains relative to the clinical isolates expressing the same CgPDR1 allele. (B) Fluconazole susceptibility testing of C. glabrata clinical isolates DSY2235 and DSY2234, revertant strains (rev) overexpressing CgPDR1 alleles and of a pdr1Δ mutant (SFY53). Isolates were grown on YPD medium containing the drug at the indicated concentration at 30°C for two days. (C) Immunodetection of CgCdr1p and CgCdr2p in C. glabrata clinical isolates DSY2235 and DSY2234, in revertant strains (rev) overexpressing CgPDR1 alleles in a pdr1Δ mutant (SFY53). Proteins extract were separated by SDS-10% PAGE and immunoblotted with rabbit polyclonal anti-CgCdr1p and anti-CgCdr2p antibodies as described previously [9]. MICs to fluconazole were determined by broth microdilution method in accordance with the CLSI M27-A2 document (National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, 2002).