Figure 1.
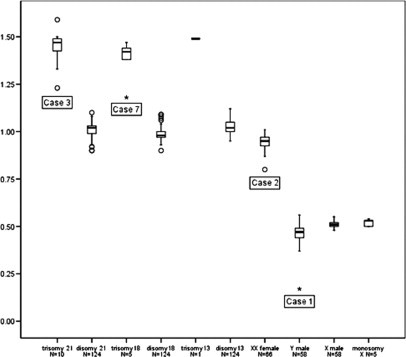
Quantitative MLPA analysis with mean probe ratios of the 21, 18, 13, X, and Y targets with 50% of the samples within the box. The outliers are cases ‘o’ with values between 1.5 and 3 box-lengths from the boundaries of the box. Case 3 shows an increased mean probe ratio for chromosome 21 of 1.24 (95% CI, 1.02−1.46). Inspection of individual probe ratios of this chromosome showed an increase for all individual probes, indicative for a mosaic of trisomy 21. Case 7 is illustrated as an extreme (*) in the box plot with an increased mean probe ratio for chromosome 18 of 1.18 (95% CI, 1.08−1.28), ie, this ratio is increased for the expected value of 1.0 for a disomy 18 and decreased for the expected ratio of 1.5 for a trisomy and, therefore, indicative for a mosaic trisomy 18. Case 1 is illustrated as an extreme (*) in the box plot with a mean probe ratio for the Y chromosome of 0.17 (95% CI, 0.14−0.21). Case 2 is illustrated as an outlier ‘o’. The mean probe ratio for X is 0.80 (95% CI, 0.70−0.90), ie, this ratio is increased for the expected value of 0.5 for a monosomy X and decreased for the expected ratio of 1.0 for a disomy and, therefore, indicative for a mosaic 45,X/46,XX. The other outliers in the box plots result in increased or decreased mean probe ratios, all related to broad confidence intervals. The expected values of 0.5, 1.0, or 1.5 are within the confidence intervals in all outliers.
