Abstract
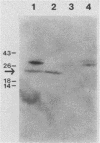
Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) isolated from the growth medium of Staphylococcus aureus 1169 and 555 was used to immunize male rabbits before infection with either a TSST-1+ or a TSST-1- strain of S. aureus isolated from cases of TSS. None of the immunized rabbits died as a result of the infections, whereas 50% of the nonimmunized rabbits infected with the TSST-1- strain, D4508, and 75% of those infected with the TSST-1+ strain, 555, died. Western blots of crude extracellular protein preparations probed with sera from immunized rabbits indicated that the TSST-1- strain produces a 30,000-molecular-weight protein that cross-reacts with antiserum to TSST-1. Because both organisms caused similar diseases in rabbits, we propose to designate the cross-reacting protein as TSST-2.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arko R. J., Rasheed J. K., Broome C. V., Chandler F. W., Paris A. L. A rabbit model of toxic shock syndrome: clinicopathological features. J Infect. 1984 May;8(3):205–211. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)93859-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best G. K., Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Crowell W. F., Kirkland J. J. Enhanced susceptibility of male rabbits to infection with a toxic shock strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):727–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.727-732.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Falkow S. Protein antigens from Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic-shock syndrome. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7466361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbe P. L., Arko R. J., Reingold A. L., Graves L. M., Hayes P. S., Hightower A. W., Chandler F. W., Broome C. V. Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. Evidence for additional toxins. JAMA. 1985 May 3;253(17):2538–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejima T., Dinarello C. A., Gill D. M., Wolff S. M. Induction of human interleukin-1 by a product of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1312–1320. doi: 10.1172/JCI111334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Dufrenne J. B. A simple purification method for enterotoxin F produced by Staphylococcus aureus and some properties of the toxin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1982 Dec;48(5):447–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00448416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Antigen-antibody reactions in gels. IV. Types of reactions in coordinated systems of diffusion. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;32(2):230–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed J. K., Arko R. J., Feeley J. C., Chandler F. W., Thornsberry C., Gibson R. J., Cohen M. L., Jeffries C. D., Broome C. V. Acquired ability of Staphylococcus aureus to produce toxic shock-associated protein and resulting illness in a rabbit model. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):598–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.598-604.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser J., Wardale J. Immunological detection of specific proteins in total cell extracts by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazophenylthioether paper. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar;114(3):569–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart J., Reiser J., Stark G. R. Transfer of proteins from gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection with antisera: a method for studying antibody specificity and antigen structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Kirkland J. J., Best G. K. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with toxic shock syndrome, using polyethylene infection chambers in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):383–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.383-387.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Peralta J. M., Simons A. R. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:377–391. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. W. Host-parasite factors in group A streptococcal infections. Pyrogenic and other effects of immunologic distinct exotoxins related to scarlet fever toxins. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:255–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zettergren J. G., Leifer M. J., Nakashima H., Wuepper K. D. Human mononuclear leukocyte transglutaminase activity is enhanced by streptococcal erythrogenic toxin and a staphylococcal mitogenic factor associated with toxic shock syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 20;802(3):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]