Abstract
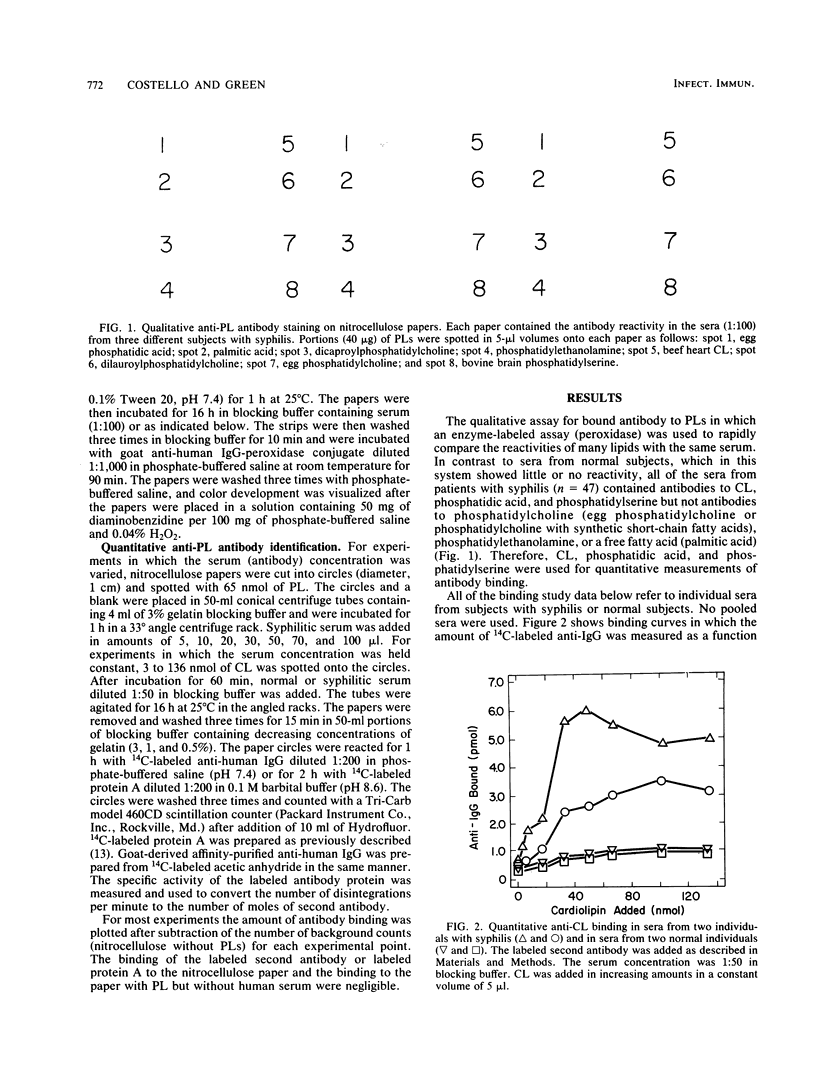
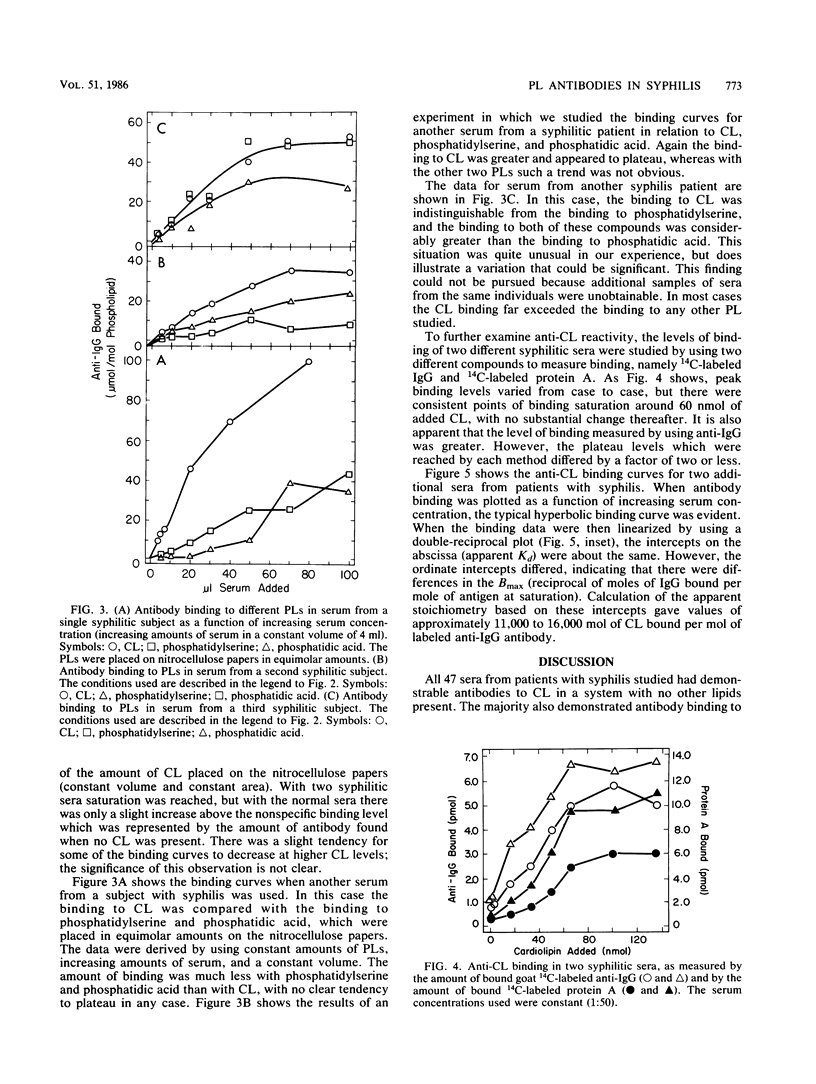
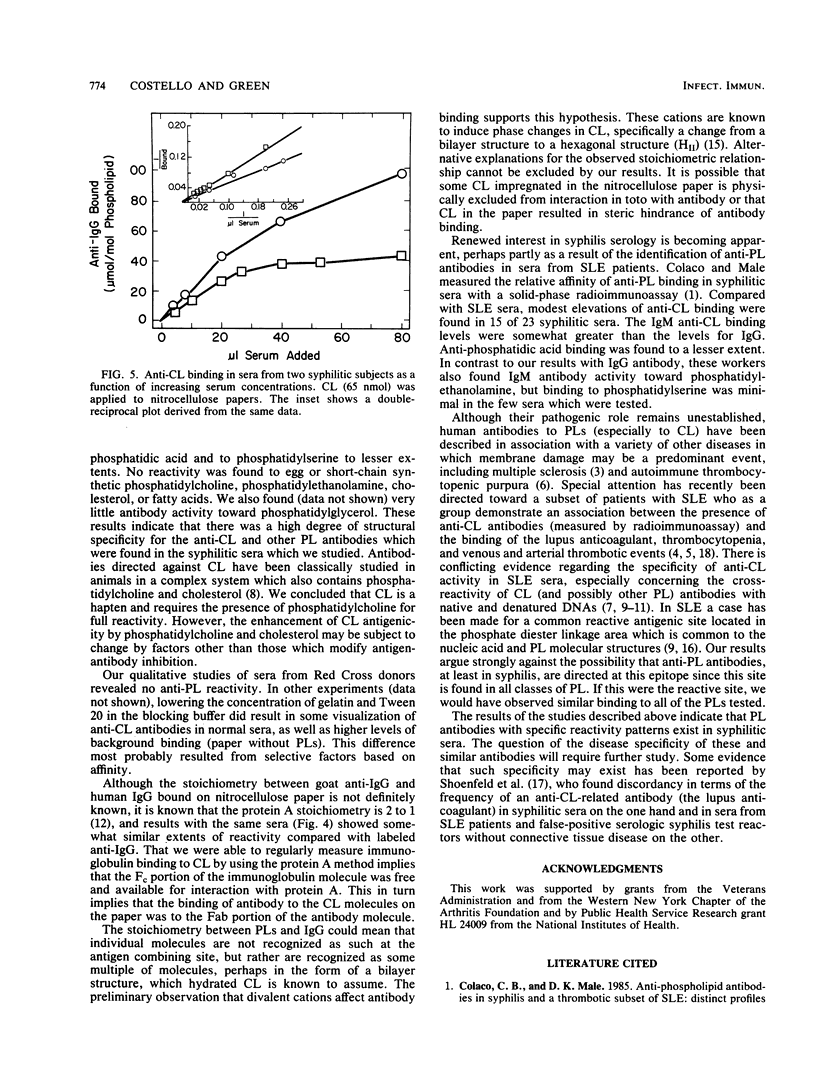
Sera from patients with proven cases of syphilis were tested for the presence of antibodies to structurally important phospholipids by using qualitative and quantitative assays. All 47 sera examined qualitatively contained antibodies to cardiolipin, phosphatidic acid, and phosphatidylserine, but not antibodies to other selected phospholipids. Such reactivity was not found in normal (Red Cross) sera. Although the degree of antibody binding to phospholipids varied in individual sera, reactivity was almost always greater with cardiolipin than with phosphatidic acid or phosphatidylserine. Binding saturability was found in sera as the cardiolipin concentration was increased over a constant area of nitrocellulose paper. Anti-cardiolipin binding measured by the protein A method gave results similar to the results measured by using anti-immunoglobulin G, which supports the conclusion that binding was to the Fab portion of the immunoglobulin molecule. When measured as a function of serum concentration and plotted in double-reciprocal fashion, the anti-cardiolipin binding data for two syphilitic sera had similar Kd values but different Bmax values. Stoichiometric calculations indicated that approximately 11,000 to 16,000 mol of cardiolipin appeared to be bound per mole of labeled second antibody. These observations may mean that the anti-cardiolipin antibody does not recognize the individual cardiolipin molecule as the antigenic site but recognizes some structural form of the phospholipid or that steric hindrance related to the interaction of the phospholipid with nitrocellulose paper prevented the bulk of cardiolipin molecules from reaching. The structural specificity of the antibodies identified excludes the possibility that these antibodies are directed against the phosphodiester linkage. These findings should give impetus to future study of a potential pathogenic or marker role for these antibodies in syphilis and in other syndromes in which membrane damage may be a primary event.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Endo T., Scott D. D., Stewart S. S., Kundu S. K., Marcus D. M. Antibodies to glycosphingolipids in patients with multiple sclerosis and SLE. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1793–1797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englert H. J., Hawkes C. H., Boey M. L., Derue G. J., Loizou S., Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Hull R. G., Hughes G. R. Degos' disease: association with anticardiolipin antibodies and the lupus anticoagulant. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Sep 8;289(6445):576–576. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6445.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Asherson R. A., Boey M. L., Hughes G. R. Cerebral infarction in systemic lupus: association with anticardiolipin antibodies. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1984 Jan-Mar;2(1):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Hegde U., Derue G., Morgan S. H., Englert H., Chan J. K., Asherson R. A., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies in autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1985 Feb;59(2):231–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Hughes G. R. Comment on Isenberg article (Multiple serologic reactions and their relationship to clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus) Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Nov;27(11):1318–1318. doi: 10.1002/art.1780271123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Nojima S. Immunochemical studies of phospholipids. 3. Production of antibody to cardiolipin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Schwartz R. S. Multiple serologic reactions and their relationship to clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Feb;27(2):132–138. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Tomioka H., Kumagai A. Antibodies cross-reactive with DNA and cardiolipin in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):298–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Rauch J., Andrzejewski C., Jr, Mudd D., Furie B., Furie B., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Polyspecific monoclonal lupus autoantibodies reactive with both polynucleotides and phospholipids. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):897–909. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and related immunoglobulin receptors produced by streptococci and pneumonococci. Adv Immunol. 1982;32:157–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens N. A., Hui H. L., Green F. A. The binding characteristics of anti-Rho(D)-positive human and chimpanzee erythrocytes measured with 14C protein A. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1471–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Sengupta S. Cardiolipin forms hexagonal structures with divalent cations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 11;255(2):484–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Schwartz R. S. Immunologic and genetic factors in autoimmune diseases. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 18;311(16):1019–1029. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410183111605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Shaulian E., Shaklai M., Kruglack J., Feuerman E., Pinkhas J. Circulating anticoagulant and serological tests for syphilis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1980;60(4):365–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr Cerebral infarction in systemic lupus: association with anticardiolipin antibodies. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1984 Jan-Mar;2(1):3–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haas G. H., van Deenen L. L. Chemical structure and serological activity of synthetic and natural cardiolipin. Nature. 1965 May 29;206(987):935–935. doi: 10.1038/206935a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



