Fig. 3.
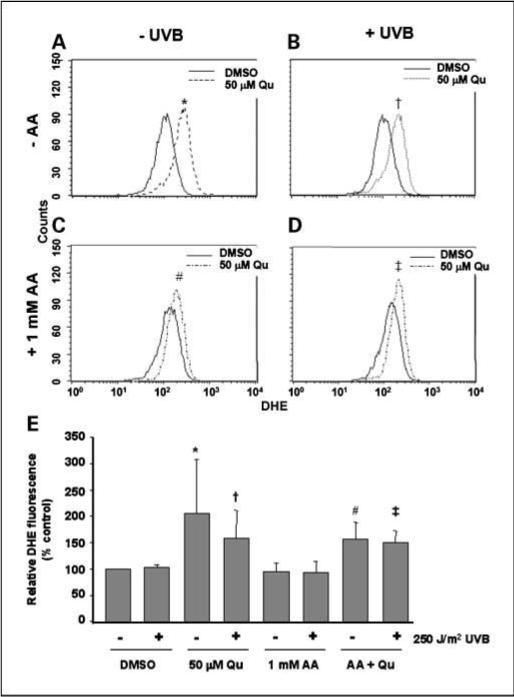
Qu acts as an oxidant by generating reactive species. HaCaT cells were treated with 50 μmol/L Qu in the presence or absence of 1 μmol/L AA for 1 h before UVB irradiation. After exposure to UVB, cells were placed back in DMEM containing appropriate treatments for 1 h. During this time, 10 μmol/L dihydroethidium (DHE) was added to the medium to measure the generation of reactive species. Generation of ROS was then determined by flow cytometry (A–D). Treatment with Qu caused significant oxidation of dihydroethidium in both mock-irradiated and UVB-irradiated cells regardless of the presence of AA. E, the data were pooled from five independent experiments each measuring a total of 10,000 events. Columns, mean; bars, SD. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05 using one-tailed t test: *, versus DMSO-UVB; †, versus DMSO + UVB; #, versus AA-UVB; ‡, versus AA + UVB. No statistical significance was found between any Qu-treated condition regardless of the presence of AA.
