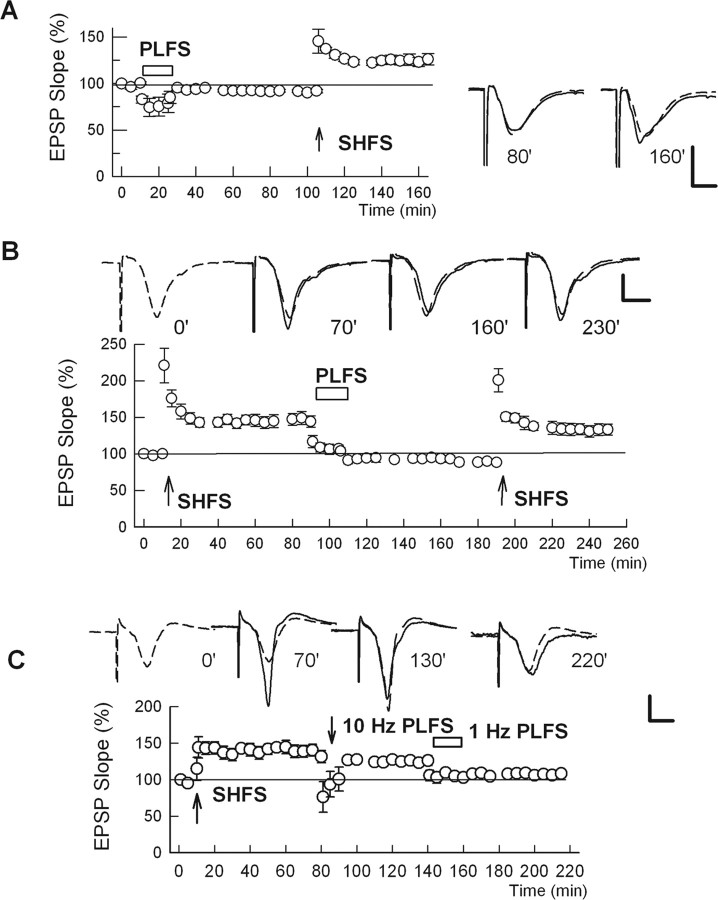
Figure 2.
Effects of PP stimulation on synaptic plasticity in the SC pathway. A, LFS of the PP (PLFS) causes a transient depression of SC transmission that rapidly recovers after PLFS. A subsequent 100 Hz by 1 s HFS of the SC inputs (SHFS) results in LTP. B, After induction of SC LTP, PLFS results in rapid depotentiation of SC inputs. A subsequent tetanus delivered to the SC results in a return of LTP. Traces above the graph show EPSPs obtained at the times denoted, with the initial baseline response shown as a dashed trace in the last three panels. C, Depotentiation of SC LTP by PP stimulation is frequency dependent. After establishing SC LTP, 10 Hz by 900 pulse stimulation of the PP causes only a transient depression of LTP. In contrast, subsequent 1 Hz PLFS results in depotentiation. Error bars indicate SEM. Traces above the graph show representative EPSPs. Calibration: 1 mV, 5 ms.