Fig. 2.
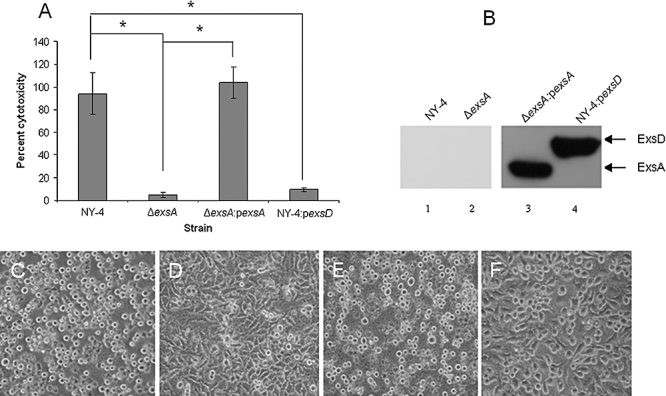
Mutation of exsA gene and overexpression of exsD gene in wild-type strains attenuated the ability of V. parahaemolyticus to induce host cell death.
A. HeLa cells were lysed by wild-type (NY-4) and exsA complement (ΔexsA : pexsA) strains of V. parahaemolyticus while strain ΔexsA and wild-type strain transformed with exsD plasmid (NY-4 : pexsD) had significantly lower levels of cytotoxicity against HeLa cells (bars = standard deviation for three replicates; star represents statistical difference P < 0.05).
B. Expression of exsA and exsD in ΔexsA and wild-type strains respectively. Anti-His antibody detected the ExsA and ExsD in the strains of ΔexsA : pexsA and NY-4 : pexsD respectively (Lanes 3 and 4), but not in the wild-type or ΔexsA controls. Morphological observations under light microscope for HeLa cells infected with (C) NY-4 strain, (D) ΔexsA strain, (E) ΔexsA : pexsA strain and (F) NY-4 : pexsD strain.
