Fig. 1.
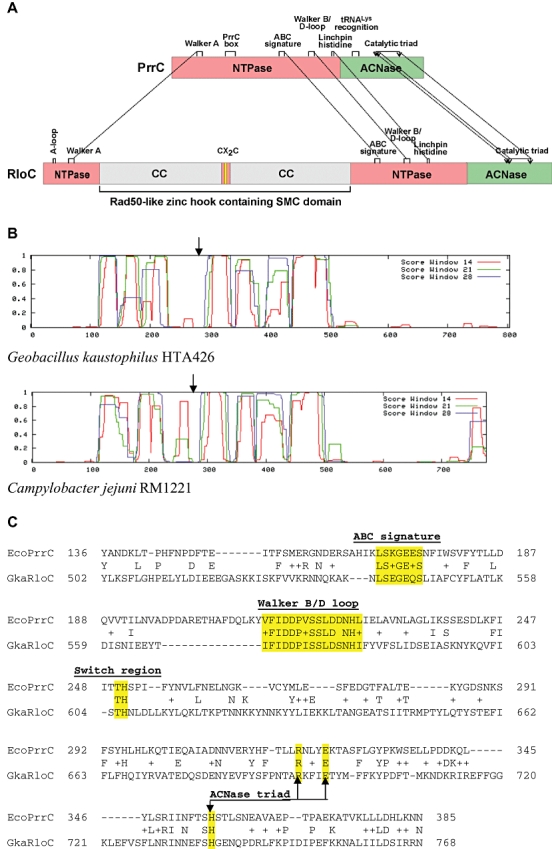
Functional organization of PrrC and RloC.
A. Domain alignment. The ATPase domain of PrrC and ATPase head domain of RloC are indicated by pink rectangles, the ACNase domains by green rectangles; predicted α-helical regions flanking the CXXC zinc-hook motif thought to form an antiparallel coiled-coil bundle (CC) (Hopfner et al., 2002) are in grey, the gap containing the CXXC motif is in pink and the motif itself is in yellow. Dashed lines connect motifs shared by PrrC and RloC including the Walker A (P-loop), ABC signature, Walker B/D-loop, linchpin histidine/switch region (Moody and Thomas, 2005) and catalytic ACNase triad (Blanga-Kanfi et al., 2006). The A-loop [base specificity motif of typical ABC ATPases (Ambudkar et al., 2006)] is missing from PrrC whereas the PrrC Box (Blanga-Kanfi et al., 2006) and the region implicated in tRNA recognition have been described only in PrrC (Klaiman et al., 2007).
B. COILED-COIL predictions of RloC orthologues encoded by the indicated bacterial strains. The arrow points at the position of the CXXC motif.
C. Alignment of selected E. coli PrrC and G. kaustophilus HTA426 RloC sequences containing shared functional motifs (highlighted).
