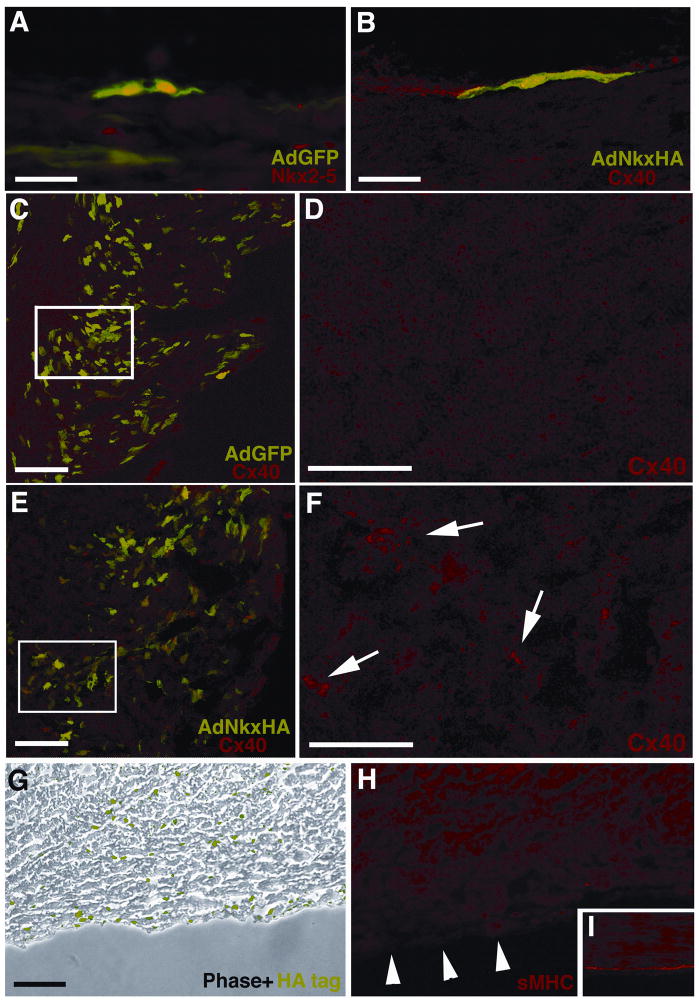
Figure 4. Over-expression of Nkx2-5 in vivo perturbs AVCS development.
Hearts microinjected at E10 with various constructs were harvested at E18. GFP fluorescence and immunohistochemistry was used to analyze heart sections for AVCS markers. (A) Control vector GFP expression alone does not disrupt the normal nuclear Nkx2-5 expression (TRITC) of SPFs at E18. (B) In this single GFP positive SPF over-expression of Nkx2-5 by AdNkxHA does not disrupt Cx40 expression (TRITC). (C) Low magnification image of RV myocardium labeled with GFP and immunostained with Cx40, which only localizes to SPFs. (D) Enlargement of boxed area in (C) revealing little Cx40 immunolabeling of the myocardium. (E) Low magnification image of RV myocardium labeled with GFP (indicating AdNkxHA infection) and immunostained with Cx40 showing that ectopic Cx40 localizes with GFP expression in the myocardium. (F) In contrast to D ectopic Cx40 immunolabeling is present (arrows) within this enlarged image of boxed area in E. (G) Immunolabeling for HA-tag reveals abundant Nkx2-5 over-expression within AdNkxHA infected tissue (phase contrast, HA-tag in green). (H) A sister section to G shows reduced sMHC immunostaining in the sub-endocardium (arrowheads). (I) Control tissue shows typical sMHC staining of sub-endocardial Purkinje fibers. Scale bars 50 μm (A, B, D, F), 100 μm (C, E, G, H, I).