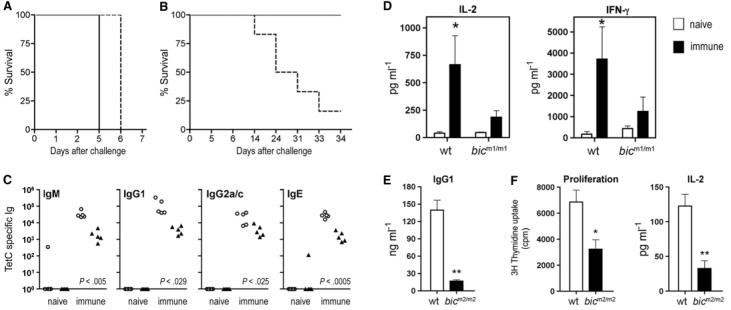
Fig. 2.
Defective adaptive immunity by bic-deficient mice. (A) Survival curve for mice (n = 5 in each group) infected orally with 1 × 108 colony-forming units (CFU)–virulent S. typhimurium strain SL344. As expected for mice of this genetic background, all failed to survive challenge. (B) Survival of mice (n = 6 in each group) infected intravenously with 1 × 104 CFU of S. typhimurium aroA strain followed by oral challenge with S. typhimurium SL344 6 weeks after prime. In contrast with control mice, bicm2/m2 mice demonstrate reduced survival after challenge. (A and B) Line, control C57BL/6J (wild-type) mice; dashed line, N5 C57BL/6J backcross bicm2/m2 mice. (C) TetC-specific Ig levels from control mice (open circles) or bic-deficient mice (filled triangles) immunized with TetC at days 1 and 21 and analyzed 13 days after secondary immunization. P values denote significant differences; Student's two-tailed t test. (D) Production of IL-2 and IFN-γ by splenocytes isolated from wild-type or bicm1/m1-naïve mice (open bars) or immunized with TetC as in (C) (closed bars) and cultured for 48 hours in the presence of TetC. Data are the mean ± SE from four mice. *P < 0.05 versus naïve mice; Student's two-tailed t test. (E) Reduced IgG1 production by bicm2/m2 B cells cultured in the presence of LPS and IL-4 for 4 days. Data are the mean + SE from 3 mice. **P < 0.01 versus wild-type; Student's two-tailed t test. (F) Significantly reduced proliferation and IL-2 production by ovalbumin T cell receptor transgenic (OT-II) cells cultured with LPS-matured, bone marrow–derived, bic-deficient DCs in the presence of cognate (2.5 μM) ovalbumin protein. Cell proliferation was determined by [3H]-thymidine incorporation at 72 hours. IL-2 was measured from supernatants by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) at 48 hours. Data are the mean + SE from five mice of each genotype. *P < 0.05 versus wild-type; Student's two-tailed t test.