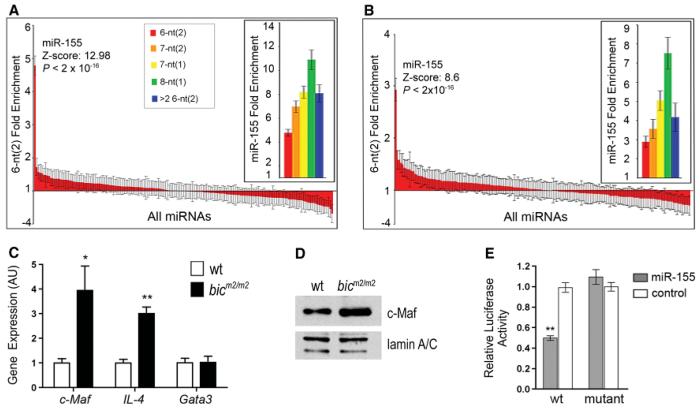
Fig. 4.
miR-155 pattern sequences are enriched in the Th1 and Th2 cell up-regulated genes, and c-Maf is a bona fide target of miR-155. (A and B) Fold enrichment of 5′ miRNA pattern sequences of the indicated types contained in the 3′ UTRs of the (A) Th1 or (B) Th2 cDNA microarray significantly up-regulated gene sets. The standard deviation, Z score, and P value were calculated by sampling 1000 random sets of 53 (for Th1 set) or 99 (for Th2 set) genes from the mouse genome (16). Data are fold enrichment ± SD. (C) Quantitative PCR analysis for Gata3, c-Maf, and IL-4 transcript levels from Th2 cells re-stimulated with antibodies to CD3 and CD28. Data are the mean + SE from three mice. *P < 0.05 versus wild-type; Student's two-tailed t test. (D) c-MAF protein levels were assessed by Western blot of nuclear extracts of Th2 cells isolated from the indicated genotypes. Expression of lamin A/C was used as loading control. (E) miR-155–dependent repression of c-Maf reporter in vitro. A luciferase (Rluc) reporter was used to validate c-Maf as a direct target of miR-155. Wild-type (wt) or mutant plasmids (mut) were contransfected with the indicated duplex miRNA for miR-155 (open bars) or control Cel-miR-64 (filled bars) into HeLa S3 cells. Data are mean ± SE from three experiments. **P < 0.0001 in comparison with wild-type plasmid treated with nonspecific RNA duplex, Cel-miR-64; Student's two-tailed t test.