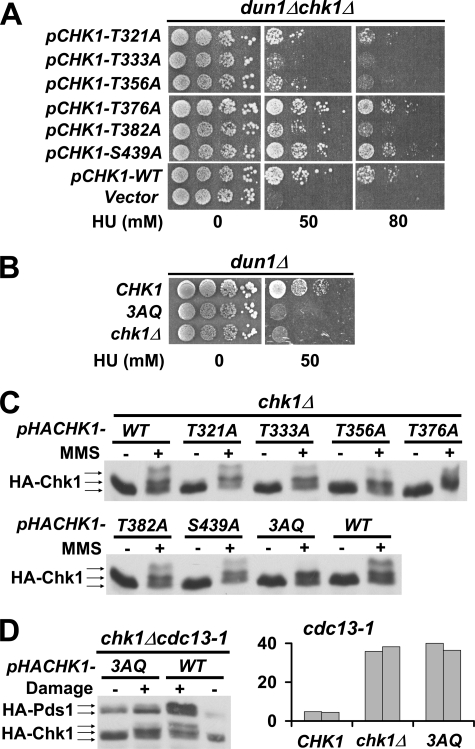
FIGURE 2.
The conserved ATRMec1 phosphorylation sites on Chk1 are essential for the checkpoint response in vivo. A, plasmids carrying Chk1 mutants with alanine substitution of threonine/serine at one of the six putative ATR Mec1 phosphorylation sites were transformed into dun1Δ chk1Δ cells. Transformants were spotted on plates containing 0 or 50 or 80 mm HU. B, the 3AQ mutant combining three point mutations (T333A, T356A, and T382A) was integrated to the CHK1 locus in dun1Δ cells and tested for HU resistance under the same condition. C, chk1Δ cells harboring plasmids carrying HA-tagged Chk1 phosphorylation sites mutants were treated with 0.1% MMS, and protein extracts were analyzed by Western blots using anti-HA antibody. D, left, plasmids carrying HA-tagged 3AQ mutant were introduced into cdc13-1 chk1Δ cells, and DNA damage was elicited by incubating the cells at the nonpermissive temperature. The mobility shifts of Chk1 and accumulation of Pds1 were monitored by Western blots. Right, the 3AQ mutant was integrated into cdc13-1 cells, and checkpoint function of Chk1 in the resulting strains was evaluated using micro-colony assay. The bars represent the average number of cells per colony from 50 colonies. The experiment was carried out in duplicate.