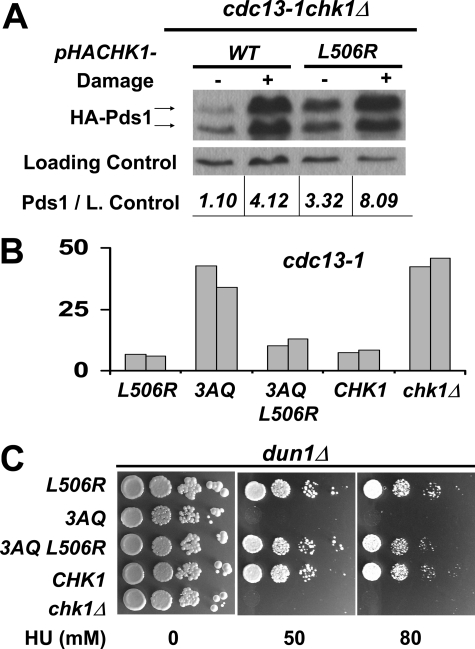
FIGURE 6.
A single amino acid substitution in the GD domain rescued the lethality of cells expressing Chk1 protein lacking the ATRMec1 phosphorylation sites. A, constructs encoding the indicated HA-tagged CHK1 alleles were transformed into a cdc13-1 chk1Δ HA-PDS1 yeast strain, and transformants were grown at the permissive temperature (no DNA damage) and restrictive temperature (DNA damage) for cdc13-1. Chk1 and Pds1 were visualized by Western analysis using anti-HA antibodies. B, Chk1 mutants 3AQ, L506R, and the combined mutants 3AQ L506R were integrated into cdc13-1 cells. The resulting strains were evaluated for checkpoint function by micro-colony assay. The bars represent the average number of cells per micro-colony from 100 micro-colonies. C, the same chk1 alleles were also integrated into dun1Δcells and evaluated for growth on HU.