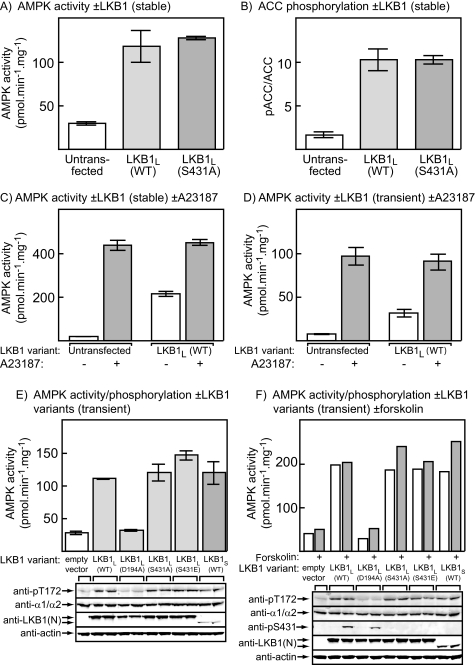
FIGURE 1.
Effect of expression of LKB1 variants in HeLa cells. A, the activities of AMPK measured in immunoprecipitates in lysates of control cells or cells stably expressing wild type LKB1L, or the S431A mutant of LKB1L. B, as A, but measuring the phosphorylation of Ser-79 on ACC, assessed as the ratio of signal obtained by Western blotting using a phosphospecific antibody and using streptavidin to detect total ACC. C, AMPK activity in untransfected cells or cells stably expressing inactive or wild type LKB1L treated with or without 10 μm A23187. D, AMPK activity in untransfected cells or cells transiently transfected with plasmids expressing wild type LKB1L, STRADα, and MO25α, treated with or without 10 μm A23187. E, activity of AMPK (top) and expression and phosphorylation of various proteins (bottom) in HeLa cells transiently transfected with empty vector or with plasmids expressing STRADα and MO25α with LKB1L, various mutants of LKB1L, or LKB1S. The phosphorylation of AMPK at Thr-172 was assessed by probing blots with a phosphospecific antibody, as was the total level of expression of AMPK and LKB1, the latter using an antibody recognizing an N-terminal epitope that recognizes both long and short splice variants. Actin expression was also assessed as a loading control. F as E, but cells were incubated with or without 20 μm forskolin. Phosphorylation of LKB1L at Ser-431 was assessed using a phosphospecific antibody. WT, wild type.