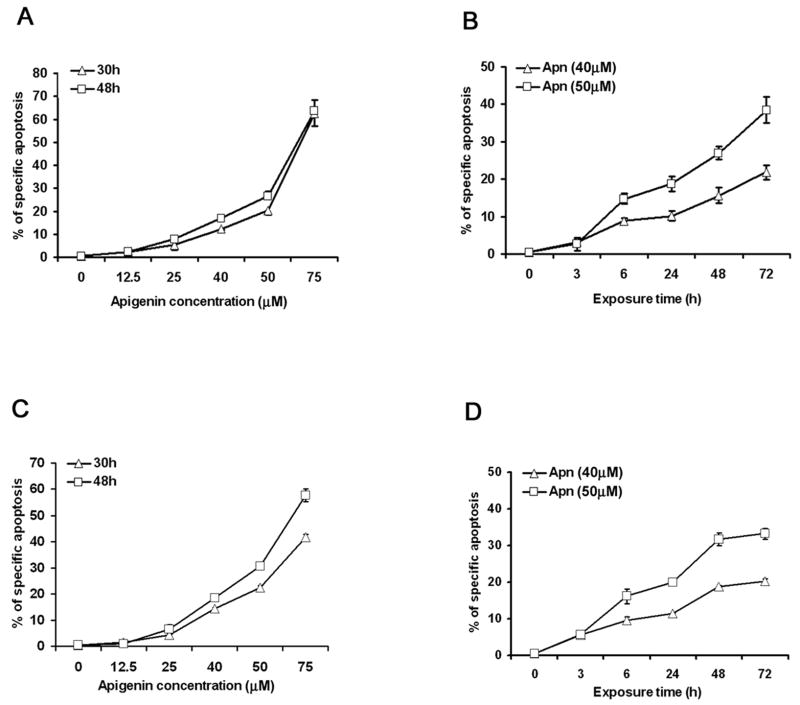
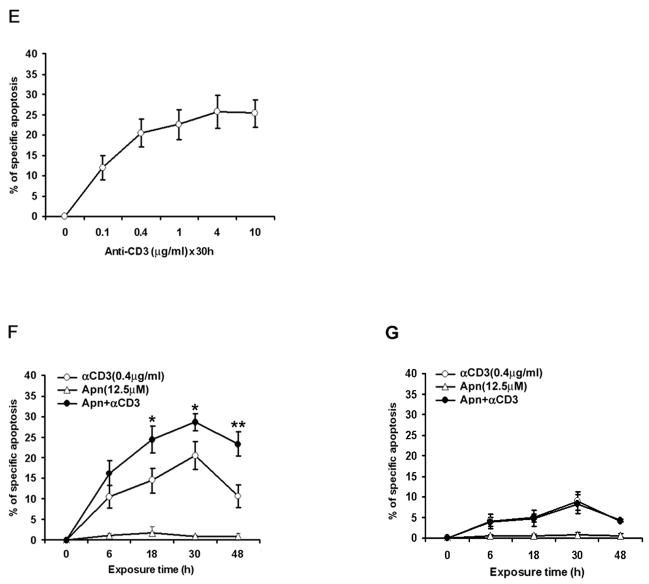
Figure 1. Apigenin enhances activation-induced cell death in human CD4 T cells.
A and B. Apigenin (Apn) causes CD4 T cell apoptosis in a dose- and a time-dependent fashion. Short-term line, CD4+ T cells derived from peripheral blood were stimulated once with plate-bounded anti-CD3 (10 μg/ml) plus anti-CD28 (1 μg/ml) for 5 days and then were rested for 7–10 days in the presence of 20 IU/ml of IL-2. The reactivated and then rested CD4+ T cells (1 × 106/ml) were treated with apigenin at indicated concentrations (A), or for various time points at fixed concentrations (B). Specific apoptosis was calculated from flow cytometry of the cells after FITC-conjugated annexin V and PI staining (See Materials and Methods).
C and D. Apigenin causes Jurkat T cell apoptosis in a dose- and a time-dependent fashion. Human Jurkat T cells (0.5 × 106/ml) were treated with apigenin at indicated concentrations (C), or for various time points at fixed concentrations (D), and apoptosis was detected as above.
E and F. Apigenin potentiates activation-induced cell death in re-stimulated human CD4 T cells. Reactivated and then rested CD4+ T cells (1 × 106/ml) from the short-term lines were re-stimulated by anti-CD3 alone in different concentrations (E), or with low-dose anti-CD3 in the presence of DMSO (vehicle control) or 12.5μM apigenin for various time points (F), and apoptosis was detected as above. Apigenin augmented anti-CD3 induce AICD in re-stimulated human T cells as early as 18 hours by about 2 folds (p<0.05). The data represent at least three independent experiments and values are mean ± SEM. * P <0.05; ** P <0.01.
G. Apigenin could not augment apoptosis in freshly obtained human CD4 T cells. Primary CD4 T cells were purified from fresh PBMCs and rested with 20u/ml IL2 overnight, those CD4 T cells (1 × 106/ml) were then stimulated for the first time by anti-CD3 (0.4μg/ml) in the presence of 12.5μM or 25μM Apigenin and 2 U/ml IL2 for various time points, and apoptosis was measured. Apoptosis in fresh human primary CD4 T cells on primary stimulation by anti-CD3 antibody was low, as compared to recurrently activated short-term line cells, and apigenin had no potentiating effect at the low dose (12.5μM) used in Fig. 1F, or ever higher doses (25 μM of Apigenin, data not shown). Experiment was repeated three times and values are mean ± S.D.