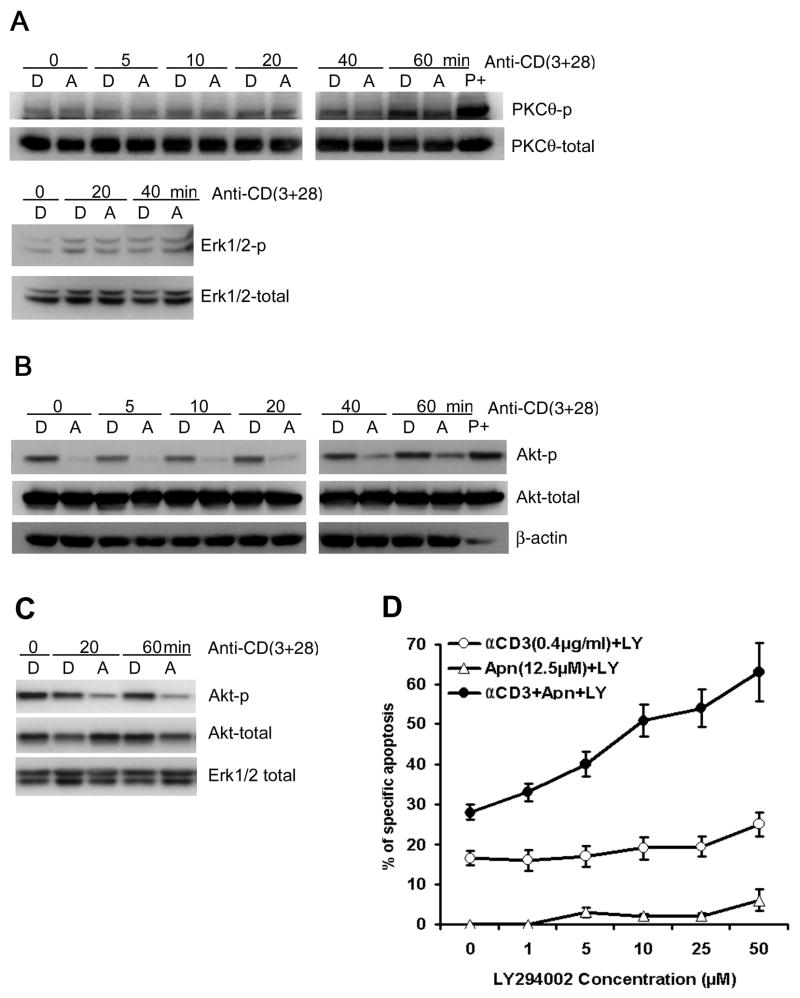
Figure 6. Apigenin inhibits PKB/Akt, but not PKC-θ or Erk phosphorylation in TCR activated human T cells.
A. Effect of apigenin on TCR re-stimulation induced activation of PKC-θ (upper panel) and MAPK Erk (lower panel). Short-term CD4 line T cells were rested and treated with 50 μM apigenin for 1.5 – 2 hours, before starting re-stimulation with anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 for different time periods, and then lysed. Activation of PKC-θ or Erk was determined by immunoblot with antibodies specific for the phosphorylated form of PKC-θ or Erk respectively. Apigenin did not significantly affect the levels of p-PKC-θ or p-Erk or the unphosphorylated total proteins.
B. Effect of apigenin on TCR stimulation-induced Akt activation in short-term line derived, CD4 T cells (2 × 106 cells/well) that were treated with 50 μM apigenin (“A”) or vehicle (“D”) for 1.5 – 2 hours before being transferred to plates coated with anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 for the indicated times. Whole-cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blot analysis with anti-phospho-Akt antibodies. The same membrane was reprobed with an anti-total Akt antibody. “P+” is positive control, as in Figure 5. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments.
C. Effect of apigenin on TCR activation-induced phosphorylation of PKB/Akt in Jurkat T cells. Jurkat T cells (1 × 106 cells/well) were treated with 50 μM apigenin (“A”) or vehicle (“D”) for 1.5 – 2 hours before transfer to plates coated with anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 for the indicated times. Whole-cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blot using anti-phospho-Akt antibody. The same membrane was reprobed with an anti-Akt Ab, and anti-Erk1/2 as a loading control. The results are representative of three independent experiments.
D. PI3K inhibitor LY294002 synergized with apigenin in augmenting anti-CD3 induced AICD in recurrently stimulated human CD4 T cells. CD4 T cells were prepared as in Fig. 1A and B. CD4+ line T cells (1 × 106/ml) were treated with plate-bound anti-CD3 (0.4μg/ml), or apigenin (12.5μM) alone, or anti-CD3 plus apigenin in the presence of LY294002 at indicated concentrations, and after 30 hours, specific apoptosis was measured as described in Fig. 1A and B. LY294002 had an additive effect on apigenin’s potentiation of AICD, in a dose dependent manner. Results represent the mean ± S.D. of three experiments.