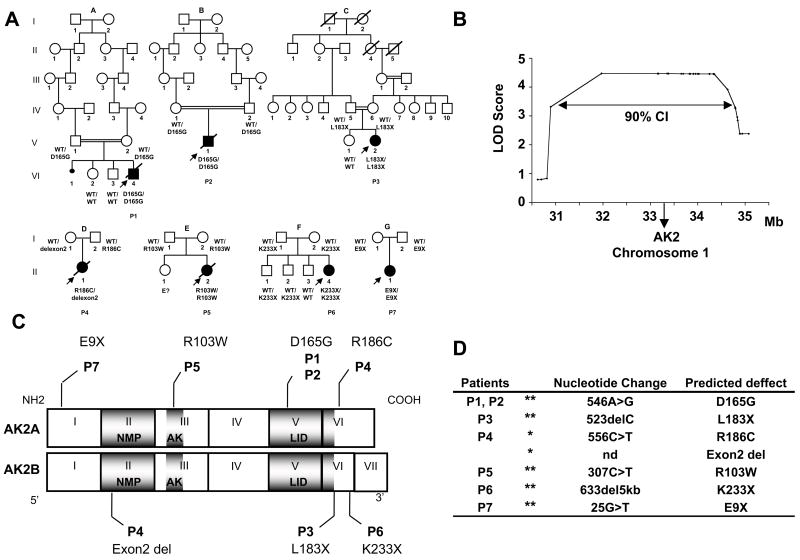
Figure 1. AK2 gene mutations in seven patients with reticular dysgenesis.
(a) Genealogical trees for 7 families with children suffering from RD (indicated by filled symbols). Diagonal bars indicate deceased individuals. Double horizontal bars indicate consanguineous marriages. AK2 mutations are indicated for each patient and parent.
WT= wild type allele of the AK2 gene. E?= no material available.
(b) Genome-wide linkage analysis Multipoint LOD scores are plotted along the 1p30–p35 region of chromosome 1. CI= confidence interval
(c) Location of AK2 mutations in RD patients. Diagrammatic representation of the AK2A and AK2B encoding regions from exon 1 to 7. The AK2A isoform includes the 6 first exons, while AK2B has an additional exon (VII). The corresponding protein domains are shown in dark grey: NMP binding domain. (NMP), adenylate kinase domain (AK) and LID domain (LID).
(d) Description of the AK2 gene mutations in the 7 RD patients. In 6 patients the mutations were homozygous (**) and in 1 patient heterozygous mutations were found (*).