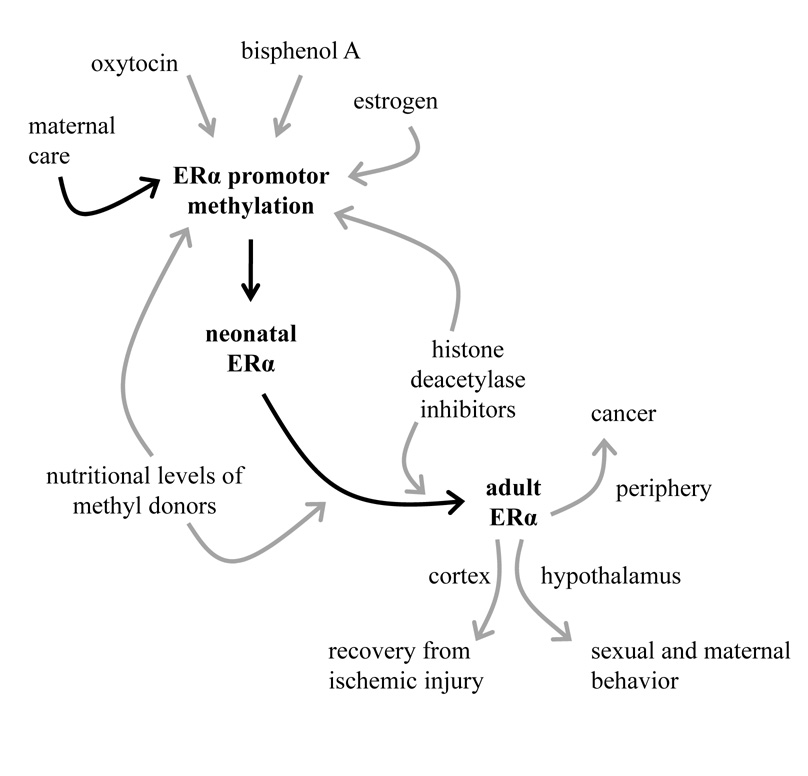
Figure 1.
Potential regulatory pathways of early environment influence on adult ERα expression. Maternal care has been demonstrated to alter site-specific ERα promotor methylation whereas neonatal oxytocin, bisphenol A and estrogen treatment have been demonstrated to exert long-term influence on ERα expression with the role of DNA methylation yet to be elucidated. Gene expression in infancy and adulthood can be modified epigenetically through dietary intake of methyl donors such as folic acid and genistein or through administration of histone deacetylase inhibitors which promote reduced DNA methylation. Consequently, adult ERα expression has site specific effects on health and behavior.