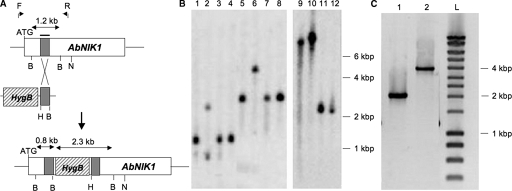
FIG. 4.
AbNIK1 gene inactivation by homologous recombination. (A) Schematic representation of the AbNIK1 locus, the LME disruption construct with the Hyg B resistance gene cassette (hatched box) and the 328-bp partial gene fragment (gray box), and the typical gene disruption mutant locus. B, BamHI; H, HindIII; N, NruI. Arrows above the AbNIK1 locus indicate the positions of the forward (F) and reverse (R) primers used for long-range PCR. (B) Southern hybridization of genomic DNA from WT isolates (lanes 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 11, and 12) and three transformants (nik1Δ1, lane 9; nik1Δ2, lane 10, and nik1Δ3, lanes 2 and 6). Each DNA set was digested with BamHI (lanes 1 to 4) or NruI (lanes 5 to 12), and the blot was probed with the 32P-labeled partial gene fragment (shown by the gray boxes in panel A). (C) Gel electrophoresis of long-range PCR products obtained from DNA of the Abra43 WT isolate (lane 1) or of the nik1Δ3 transformant (lane 2) using the flanking primers F and R. The size of DNA fragments was estimated using the DNA Smart ladder (lane L [Eurogentec, Seraing, Belgium]) and is indicated on right of panels B and C.