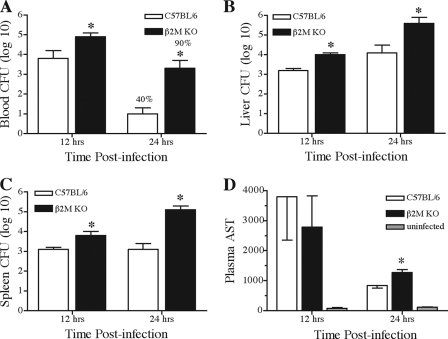
FIG. 2.
Increased bacterial burden and liver injury in β2-microglobulin-deficient mice during K. pneumoniae bacteremia. Mice were intravenously inoculated with K. pneumoniae and euthanized at the indicated time points following infection. Bacterial burdens from blood (A), liver (B), and spleen (C), along with plasma AST levels (D), were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Bacterial numbers for liver and spleen are for the entire organ, while blood bacterial numbers are per ml of blood. Data are displayed as means (with standard errors of the means) of the log10 of bacterial CFU from one (12 h) or three (24 h) independent experiments, with asterisks indicating that P was <0.005. At 24 h postinfection, the frequency of animals containing blood-borne bacteria is indicated above each bar; this difference was statistically significant (P < 0.001).