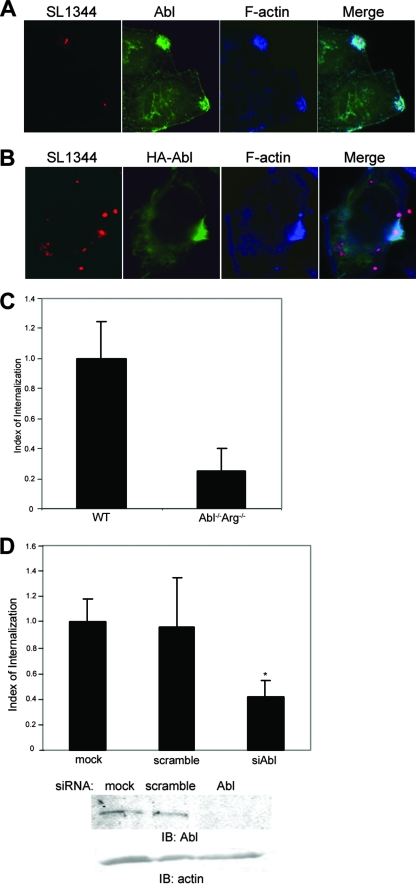
FIG. 1.
Abl family kinases are required for efficient Salmonella serovar Typhimurium internalization. (A and B) HeLa cells were infected for 30 min with WT S. enterica serovar Typhimurium strain SL1344 expressing DsRed and then fixed and stained for either endogenous c-Abl (A) or exogenous HA-tagged c-Abl (B) (green). Sites of active invasion were detected with Alexa 647-conjugated phalloidin (blue). (C) WT MEFs or isogenic cells lacking c-Abl and Arg (Abl−/− Arg−/−) were infected with SL1344 for 30 min. Internalization efficiency was quantified by using the two-color immunofluorescence assay described in Materials and Methods. The number of intracellular bacteria per cell per field in WT cells was set to a value of 1, and internalization efficiency in Abl−/− Arg−/− cells is expressed as a fraction of that normalized value. Values and standard deviations were derived from the average of three independent experiments (P < 0.021). (D) HeLa cells were either depleted of endogenous c-Abl by using siRNA oligonucleotides (siAbl), mock depleted with nontargeting siRNA (scramble), or not transfected (mock). Infection and quantification of invasion efficiency were done as described in Materials and Methods. Values are normalized to the total number of internalized bacteria in the mock-treated control cells. P < 0.05. IB, immunoblotting.