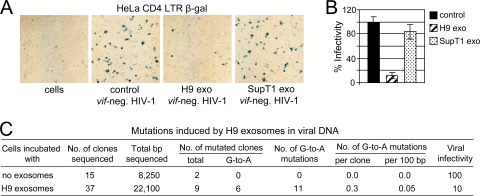
FIG. 9.
H9 exosomes reduce HIV-1 infectivity without extensive cytidine deamination in viral DNA. (A) SupT1 cells pretreated with H9 or SupT1 exosomes or not treated (control) were infected with vif-negative HIV-1, and viral supernatants were harvested on day 3 posttransfection. The same amount of viral inoculum (RT assay standardized) was added in triplicate to HeLa-CD4-LTR-β-Gal indicator cells in a 12-well plate. Three dilutions of viral inoculum were applied: 2 × 105, 2 × 104, and 2 × 103 RT cpm. After 2 days, cells were fixed and stained for β-Gal and positive syncytia (blue) were counted (B). The highest viral inoculum (2 × 105 RT cpm) applied to indicator cells is shown. Percent infectivity is presented relative to infectivity of virus produced by SupT1 cells in the absence of exosomes (100%; control). Results representative of three experiments are shown. Error bars, means ± SDs of triplicate samples. (C) Mutations induced by H9 exosomes in a 650-bp nef/3′-LTR HIV-1 DNA fragment were analyzed as described in Materials and Methods.