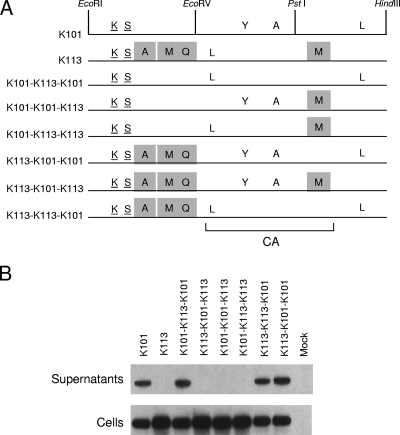
FIG. 5.
Genetic mapping of the K113 defect in viral particle production. (A) K101 and K113 Gag proteins are depicted to indicate the amino acid residues at which they differ from the K-CON Gag sequence. Underlined amino acids represent shared polymorphisms among HERV-K Gag proteins. The unique mutations in K113 Gag are indicated by shaded boxes. The restriction sites for EcoRI (R), EcoRV (V), PstI (P), and HindIII (H) were used to generate the recombinants between K101 gag and K113 gag that are shown. The bracket at the bottom shows the position of CA in Gag based on similarity to MPMV CA. (B) Western blot analysis of 293T cells transfected with 2 μg of K101, K113, or the indicated recombinant gag pCRU5 vectors was performed on both cultured supernatants and whole-cell lysates (Cells) 24 h posttransfection. The approximately 75-kDa Gag unprocessed HERV-K Gag product was visualized using a rabbit antiserum directed against HERV-K Gag, a secondary anti-rabbit-IgG-HRP antibody, and enhanced chemiluminescence.