FIG. 7.
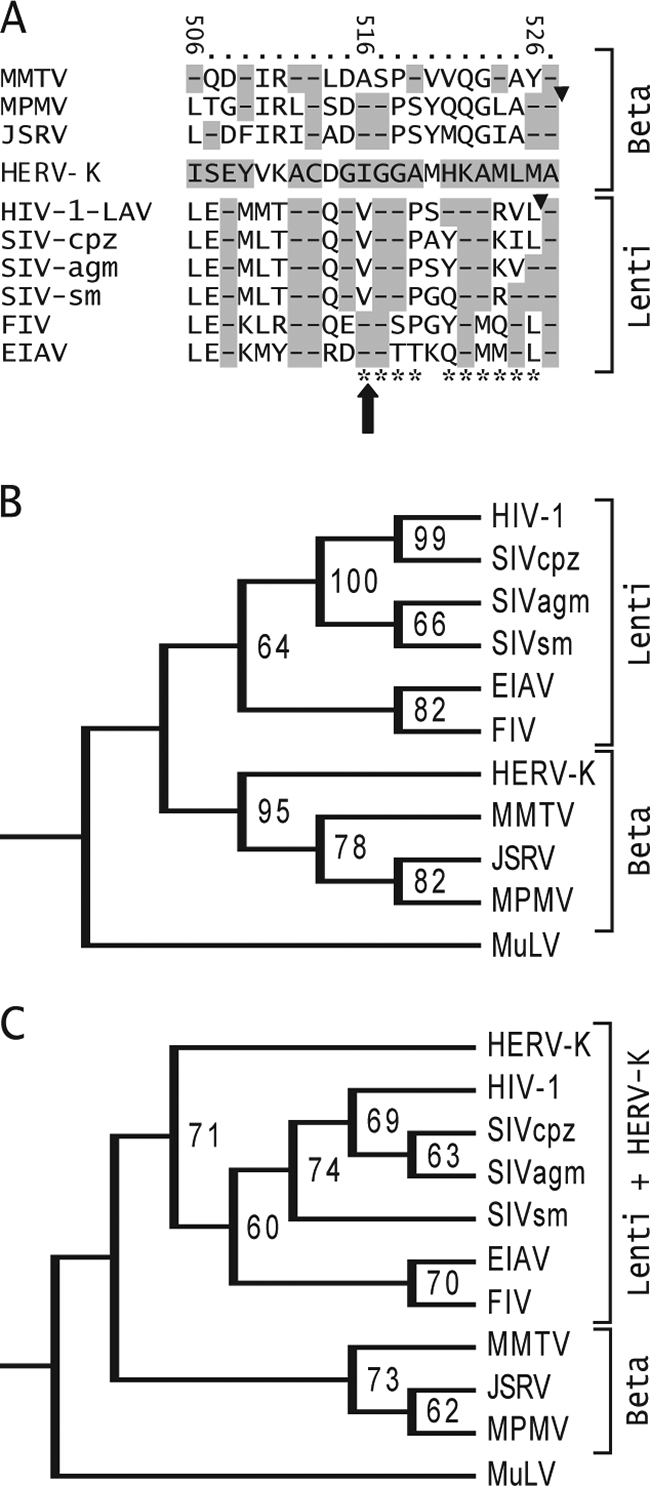
Similarity between the extreme C termini of HERV-K and other retroviruses. (A) Alignment of HERV-K Gag amino acids 506 to 527 with the corresponding Gag sequences of other retroviruses. The amino acids of HERV-K Gag are indicated, and the numbers at the top refer to position within HERV-K Gag. Other betaretroviruses are shown above HERV-K, and lentiviruses are shown below it. The large arrow shows the position of the I516M mutation unique to K113. Triangles show the positions of the protease cleavage sites that generate the C termini of MPMV and HIV-1 CA. Highlighted dashes indicate amino acid identity. The HIV-1 Gag amino acid positions identified by Melamed et al. to be highly detrimental to HIV-1 Gag particle production and infectivity are indicated by asterisks at the bottom (45). Retroviruses included in the alignment are as follows (GenBank accession numbers indicated): mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV, AAF31467), MPMV (P07567), JSRV (CAA01899), HIV-1 LAV (AAB59747), simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) from chimpanzee (SIV-cpz, AA013959), SIV from African green monkey (SIV-agm, BAF32563), SIV from sooty mangabey (SIV-sm, AAC68655), feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV, CAA48157), and equine anemia infectious virus (EIAV, AAA43011). (B) A phylogenetic tree of retrovirus CA amino acids sequences was generated using maximum parsimony in PAUP, version 4B10. Bootstrapping values were derived from 10,000 replications. The tree was rooted using the gammaretrovirus Moloney murine leukemia virus (AAB59942) as the outlier. (C) Tree generated using maximum parsimony on the amino acids at the extreme C terminus of CA. The sequences shown in panel A were used, along with the corresponding amino acids of Moloney murine leukemia virus (AAB59942) as the outlier.
