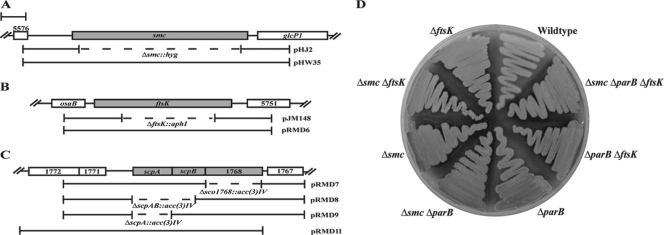
FIG. 1.
Physical maps of regions of chromosomal DNA containing smc, ftsK, or scpAB. In each case, the flanking genes are in the same orientation as the genes of interest. Bar: 1 kb. (A) The smc region of the chromosome. SCO5576 is predicted to encode an acyl phosphatase and glcP1 is involved in glucose uptake. For mutagenic plasmid pHJ2, the region deleted and replaced with a hygromycin resistance gene is shown (dashed line). The insert in complementation plasmid pHW35 is shown (bracketed line). (B) The ftsK region of the chromosome. osaB is part of a two-component regulator involved in osmoadaptation and SCO5751 is predicted to encode a hypothetical membrane protein. For mutagenic plasmid pJR148, the region of ftsK deleted and replaced with a neomycin resistance gene is shown (dashed line). The insert in complementation plasmid pRMD6 is shown (bracketed line). (C) The scpAB region of the chromosome. SCO1768, SCO1771, and SCO1767 are predicted to encode a pseudouridine synthase, a hypothetical protein found in actinomycetes, and a possible DNA hydrolase, respectively. For mutagenic cosmids pRMD7, -8, and -9, respectively, the regions of SCO1768, scpA, and scpAB deleted and replaced with an apramycin resistance gene are shown (dashed lines). The insert in complementation plasmid pRMD11 is shown (bracketed line); the DNA insert ends 1 base after SCO1768. (D) Single, double, and triple mutant strains macroscopically resemble the wild type. Strains were grown on MS agar for 4 days at 30°C. Mutant strains formed robust, gray-pigmented, aerial mycelia with no obvious growth or developmental delays. Strains M145 (wild type), J2537 (ΔparB), JM148 (ΔftsK), HJ2 (Δsmc), RMD3 (Δsmc ΔftsK), RMD4 (Δsmc ΔparB), RMD5 (ΔparB ΔftsK), and RMD6 (Δsmc ΔparB ΔftsK) are shown.