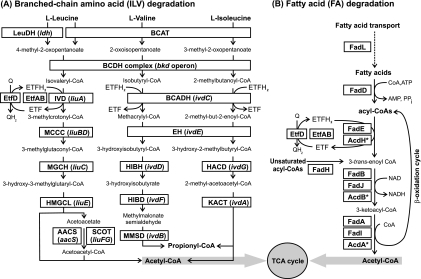
FIG. 1.
Branched-chain amino acid (A) and FA (B) catabolic pathways. (A) Abbreviations of functional roles of ILV catabolic enzymes were adopted from the respective SEED subsystems (http://seed-viewer.theseed.org/). LeuDH, leucine dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.9); BCAT, branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.42); IVD, isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.10); BCADH, branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.12); MCCC, methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase (EC 6.4.1.4); EH, enoyl-CoA hydratase (EC 4.2.1.17); MGCH, methylglutaconyl-CoA hydratase (EC 4.2.1.18); HIBH, 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.4); HACD, 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.35); HMGCL, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA lyase (EC 4.1.3.4); HIBD, 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.31); KACT, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (EC 2.3.1.16); MMSD, methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.27). The conversion of acetoacetate to acetoacetyl-CoA is mediated by either of two alternative routes: succinyl-CoA:3-ketoacid-CoA transferase (SCOT) (EC 2.8.3.5) or acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase (AACS) (EC 6.2.1.16). ECF, electron transfer flavoprotein. The assimilation of acetoacetyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA products occurs using central metabolic enzymes that are shared with other pathways (not shown). (B) FAD proteins are abbreviated according to the corresponding gene names in E. coli.